What is a Cat 5 Cable?
A Cat 5 cable, or Category 5 cable, is a type of twisted pair cable commonly used in networking and telecommunications. It was once the most popular type of Ethernet cable for local area networks (LANs), providing the necessary data transmission speeds for most networking needs. Though now largely replaced by newer standards like Cat 5e and Cat 6, Cat 5 cables are still used in some environments, particularly for older systems.

What is a Cat 5 Cable?
Key Features of Cat 5 Cable
Construction and Design:
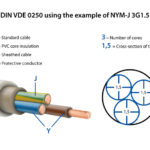
A Cat 5 cable consists of four pairs of twisted copper wires. Each pair of wires is twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between the pairs.
The wires are typically surrounded by an insulating jacket made from PVC or other materials, providing protection and durability for indoor installations.
Data Transmission Speed:
Cat 5 cables are capable of supporting speeds of up to 100 Mbps (megabits per second) and can transmit data over distances of up to 100 meters (328 feet).
While this was sufficient for many applications in the past, today’s higher-speed networks often require the enhanced capabilities offered by newer cable types like Cat 5e (which supports gigabit speeds of up to 1000 Mbps) or Cat 6.
Bandwidth:
Cat 5 cables have a maximum bandwidth of 100 MHz, which refers to the frequency range over which the cable can reliably transmit data. This is an important factor for determining how much data can pass through the cable at once, with higher bandwidth allowing for more data to be transmitted without errors.
Connector Types:
Cat 5 cables typically use the standard RJ45 connectors at both ends, which are the most common connectors used for Ethernet networks. RJ45 connectors fit into Ethernet ports on devices like computers, routers, switches, and modems.
Categories and Limitations:
While Cat 5 cables were once the standard for networking, they have been largely replaced by Cat 5e cables. Cat 5e is an enhanced version of the original Cat 5, offering better performance with reduced crosstalk and higher reliability for Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) speeds.
Cat 5 cables are typically no longer recommended for new installations, as they do not support higher speeds (such as 10 Gbps) or modern requirements like PoE (Power over Ethernet).
Common Uses of Cat 5 Cable
Basic Networking: Cat 5 cables were originally used to connect devices like computers, routers, modems, and network switches in local area networks (LANs). Although newer cables are preferred for most installations today, Cat 5 may still be used in older setups.
Telecommunications: In older systems, Cat 5 cables were used to transmit voice and data signals for telecommunications, though they have now been largely superseded by better cables like Cat 5e or Cat 6.
Residential Use: Some homes that were wired before newer standards emerged might still use Cat 5 cables for Ethernet or phone lines, though Cat 5e is more commonly found in modern homes.
Limitations of Cat 5 Cable
Speed and Bandwidth: While Cat 5 cables can handle speeds up to 100 Mbps, they are limited to lower data rates compared to more recent cable standards. For modern high-speed networks, Cat 6 or Cat 6a cables are more suitable.
Distance: Cat 5 cables are limited to distances of 100 meters for Ethernet connections. Beyond this length, the signal quality deteriorates, resulting in reduced performance or a complete loss of connection.
Crosstalk and Interference: Cat 5 cables can experience higher crosstalk (interference between the pairs of wires), which can reduce their performance. Enhanced versions like Cat 5e have improved crosstalk prevention, while Cat 6 cables have even better protection against interference.
Conclusion
A Cat 5 cable is an older type of networking cable that was once a standard for Ethernet and telecommunications systems. While it offers sufficient speed and bandwidth for basic networking needs, it has largely been replaced by Cat 5e and Cat 6 cables, which offer better performance, faster speeds, and greater reliability for modern internet and networking requirements. For new installations, it’s generally recommended to opt for Cat 5e or Cat 6 cables to ensure future-proofing and higher-speed connections. However, Cat 5 cables are still functional for older systems that don’t require the highest data speeds.