- Home
- Products
Power Cables
- Low Voltage Cables - LV
- ——Low Voltage Non-armored Copper Power Cable
- ——Low Voltage Non-armoured Aluminum Power Cable
- ——Low Voltage Steel Tape Armoured Power Cable
- Medium Voltage Cables - MV
- ——Medium Voltage Armored Power Cable
- ——Medium Voltage Non-armored Power Cable
- High Voltage Cables-HV
- Steel Wire Armored Cable (SWA Cable)
- ——Single Core AWA Armoured Cable
- ——2 Core SWA Armoured Cable
- ——3 Core SWA Armoured Cable
- ——4 Core SWA Armoured Cable
- ——5 Core SWA Armoured Cable
- ——SWA Armoured Cable Specifications
- XLPE Insulated Power Cables
- ——XLPE Insulated Single Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 2 Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 3 Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 4 Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 5 Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 3+1 Core Copper Cable
- ——XLPE Insulated 3+2 Core Copper Cable
- Mineral Insulated Cables
- TPS Cable
Renewable Energy Cables
Control & Signal Cables
- Control Cable
- Instrumentation Cable Supplier & Manufacturer
- High-Performance Coaxial Cable Supplier
- VFD Cable
Installation & Building Wire
- Premium Electrical Wire & Cable Supplier
- MC Cable
- NM-B (Non-Metallic Sheathed) Copper Wire
- UF-B Wire
- MTW Wire
Special Cables
- 4/0 Type W Cable – Heavy Duty Portable Power Solutions
- Trunk Trailer ABS Cable
- SO Cable
- Low Smoke Halogen Free Fire Resistant Cable
- Copper Ground Rods
- Copper Clad Steel Antenna Wire
- Marine Power Cords
- Extra High Voltage (EHV) Submarine Power Cables
- Submersible Pump Wire
- Floating cable
- High Temperature Wire
- EV Automotive High Voltage Silicone Rubber Cable
- Braided Stainless Steel Cable
- LC to LC Fiber Patch Cables
- Your Go-To Flexible Cable Supplier & Manufacturer
- Drag Chain Cables
- Silicone Rubber Low Temperature Resistant Cable
Overhead & Aerial Cables
- AAC Conductor
- Aerial Bundled Cable (ABC Cable) Supplier & Manufacturer
- ——NFC 33-209 ABC Cable
- ——0.6/1kV Aerial Bundle Cable
- ——Medium Voltage ABC Cable
- ——Tree Wire Spacer Cable
- ——Aluminum URD Cable
- ——Aluminum XHHW SER SEU RHH RHW-2 XLP USE-2
- Aerial Insulation Line (AIL)
- Bare Stranded Conductors Manufacturer & Supplier
- ——ACSR Conductor
- ——AAAC Conductors
- ——ACAR Conductor
- ——Bare Copper Stranded Conductor
- ——CCS Conductor
- ——ACS Condutcor
- ——Guy Wire
- Overhead Service Drop Cable / Overhead Service Wire
- ——Weatherproof Covered Line Wire
- ——Duplex Overhead Service Drop Cable
- ——Triplex Overhead Service Drop Cable
- ——Quadruplex Overhead Service Drop Cable
- Concentric Service Cable – Reliable Power Distribution Solutions
- ——Aluminum Concentric Service Cable
- ——Copper Concentric Service Cable
- ——Concentric Service Cable with Communication Pilot
- Telephone Drop Cable for Reliable Voice & Data Transmission
- ——PVC Parallel Drop Wires
- ——PE Parallel Drop Wires
- About us
- News
- Contact us
News
Stay updated with the newest developments, industry trends, and expert knowledge about various types of wires and cables. Explore our news section for valuable information and insights.
- Home
- News
Cable Ampacity Explained: How to Calculate Current Capacity (And Why It Matters)
Cable ampacity isn't a single number—it's a calculation that depends on how and where you're using the cable. Get it wrong and you risk equipment damage, fire, or code violations. Get it right and your installation is safe, efficient, and code-compliant.
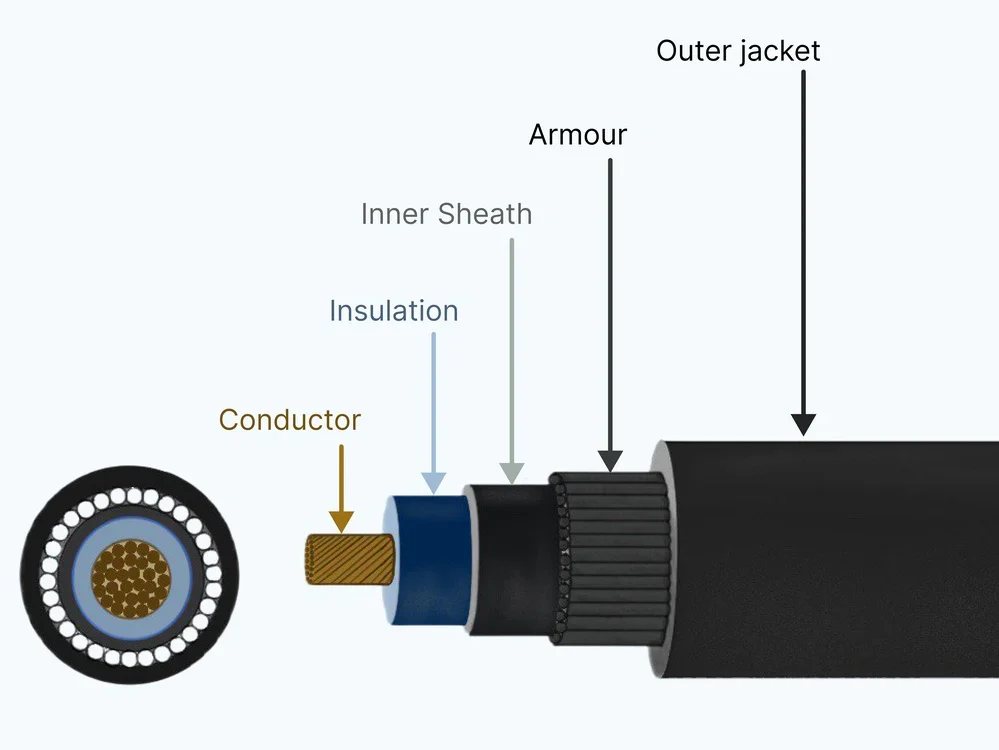
Read moreCable Construction Explained: From Conductor to Jacket (The Practical Guide)
Ever wondered why some cables cost $2 per meter while others cost $20? Or why your "heavy-duty" cable failed after six months while a cheaper one lasted five years? The answer lies in construction—the layers and materials inside the cable.
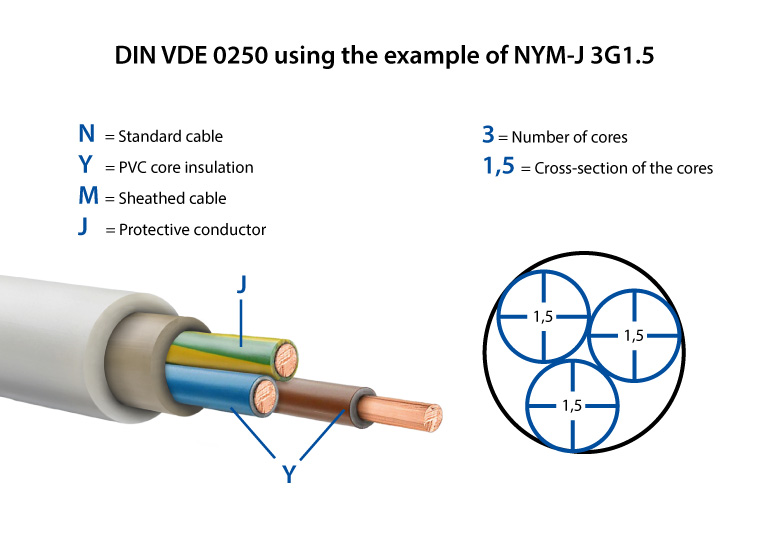
Read moreCable Designation System Decoded: Chinese GB, American NEC, and European IEC Standards Explained
Before we dive into the codes, understand this: cable designation systems exist to compress complex technical specifications into standardized shorthand.
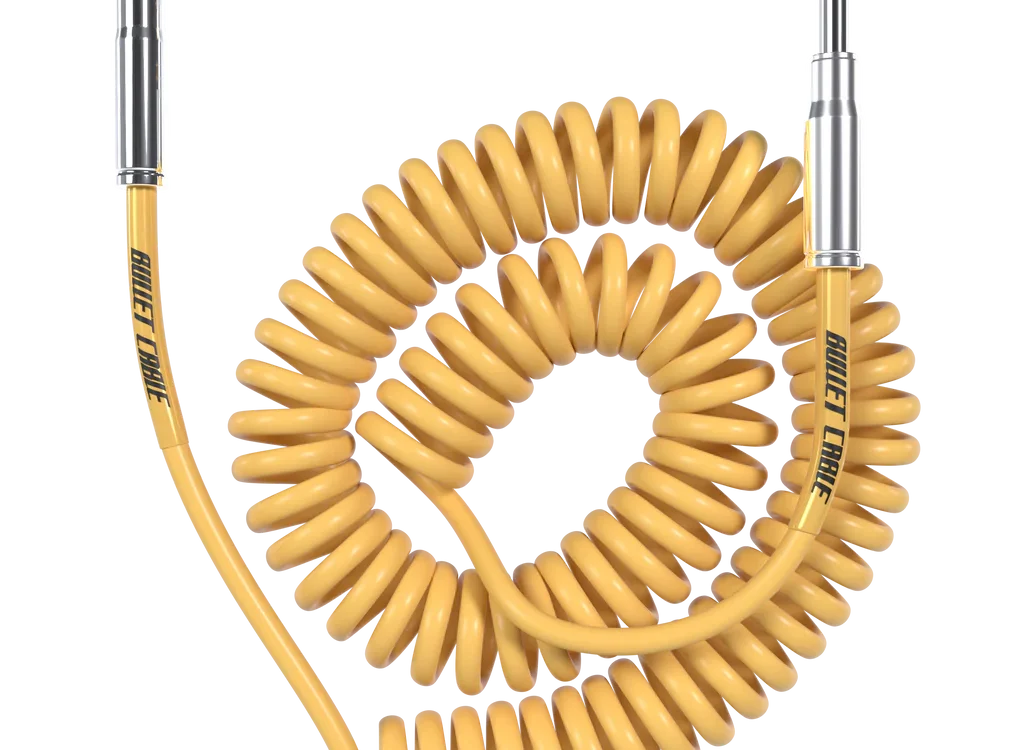
Read moreCoiled Guitar Cable vs Straight: Which One Is Actually Better for Your Rig?
You're standing in the music store, holding a coiled cable in one hand and a straight cable in the other. The coiled one looks cooler and costs twice as much. The straight one is boring but everyone says it's "better for tone." So which do you actually buy?I spent three months testing 15 different cables—coiled and straight—across multiple guitars, amps, and recording setups. I measured frequency response, tested durability, and interviewed 23 working musicians. Here's what actually matters.
Read moreCoil Instrument Cable: The Ultimate Guide for Musicians and Audio Professionals
A coil instrument cable, also known as a curly cable or spiral cable, is a specialized audio cable designed with a coiled construction that stretches and retracts. These cables have become iconic in the music industry, offering both practical functionality and distinctive aesthetic appeal for guitarists, bassists, and other musicians.
Read moreThe Science of Safety: What is Fire Retardant Material in Cable Construction?
When we talk about fire safety in electrical systems, we often focus on the standards and the results. But what actually happens inside a cable when the temperature hits 950°C? The answer lies in the flame retardant material and specialized polymers used in its construction.
Read moreUnderstanding Fire Rated Cables: Standards, Ratings, and Compliance
Selecting the correct fire resistance cable requires more than just looking at the price. By adhering to IEC and BS standards, you ensure that your fire rated cables will perform exactly when they are needed most—in the heat of a crisis.
Read moreFire Resistant vs. Flame Retardant Cables: What’s the Real Difference?
In the world of electrical engineering and building safety, the terms "fire resistant" and "flame retardant" are often used interchangeably by mistake. However, choosing the wrong one can be the difference between a minor incident and a catastrophic system failure during a fire.
Read moreAre We Underestimating Low Voltage Cables in the Sustainability Push?
The global transition to renewable energy often focuses on high-profile technologies like solar panels, wind turbines, and grid-scale batteries. However, low voltage cables—the unsung workhorses of power distribution—play a critical role in ensuring energy efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Their importance is frequently overlooked, yet advancements in LV technology could unlock significant gains in the sustainability of modern energy systems.
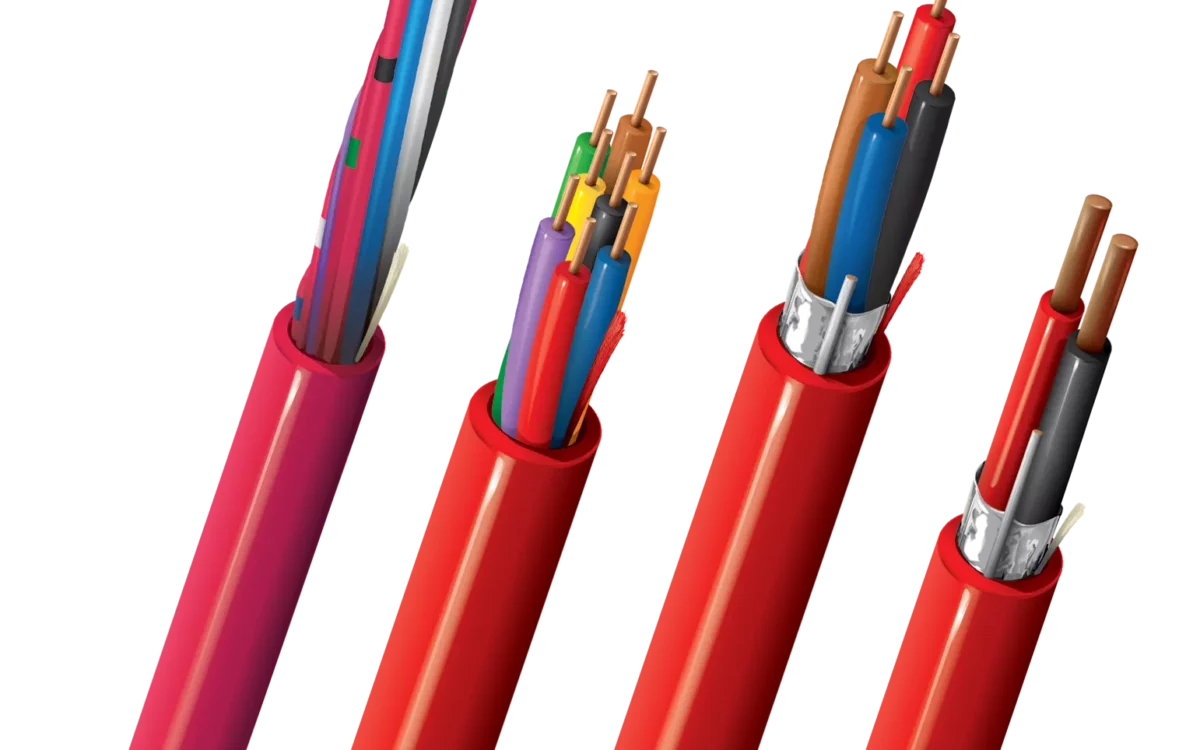
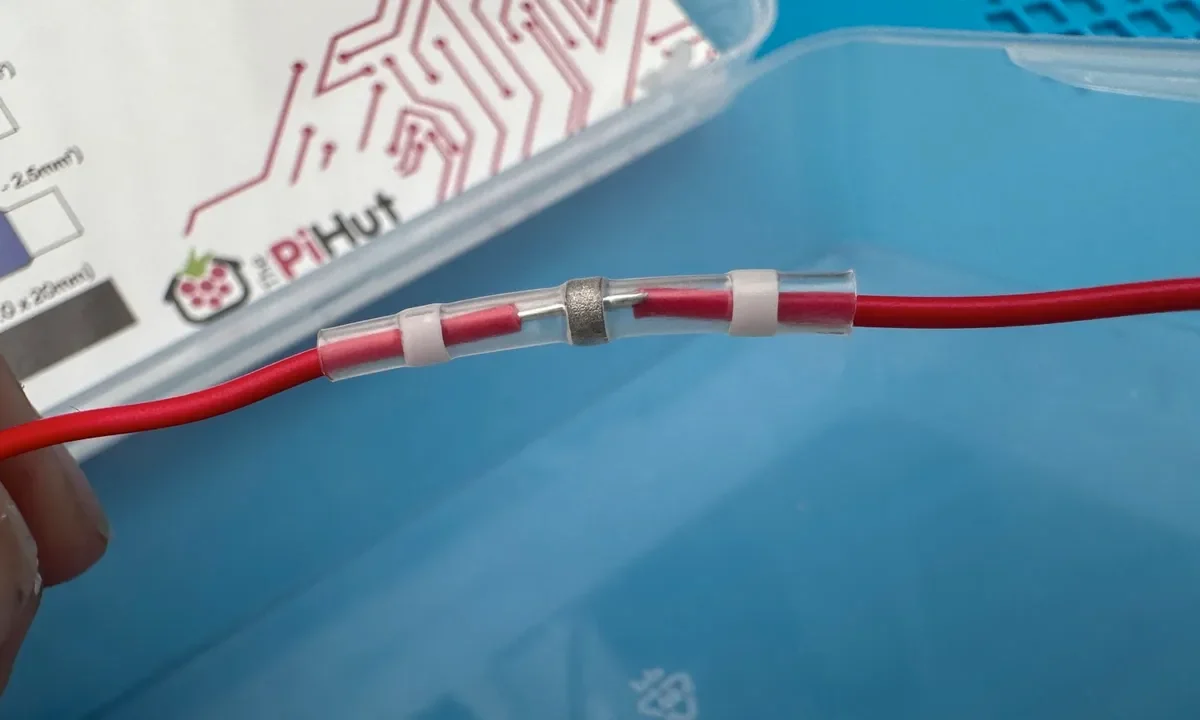
Read moreHow to Fix a Broken Wire Without Soldering
A broken or cut electrical wire can be frustrating, but in many situations you don’t need soldering to make a safe and reliable repair. With the right tools and techniques, you can fix damaged electrical wires quickly and effectively—whether it’s a household cord, automotive wire, or low-voltage cable.
Read more- Low Voltage Cables – LV
- Medium Voltage Cables – MV
- High Voltage Cables-HV
- Steel Wire Armored Cable (SWA Cable)
- XLPE Insulated Power Cables
- Mineral Insulated Cable (MICC/MI Cable)
- TPS Cable
- Control Cable
- Instrumentation Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- VFD Cable
- Computer Cable
- Electrical Wire
- MC Cable
- NM-B (Non-Metallic Sheathed) Copper Wire
- UF-B Underground Feeder Cable
- MTW Wire
- Prefabricated branch cables
- 4/0 Type W Cable
- Trunk Trailer ABS Cable
- SO Cable
- LSZH Cable
- Copper Ground Rods
- Copper Clad Steel Antenna Wire
- High Temperature Wire
- EV Automotive High Voltage Silicone Rubber Cable
- Submersible Pump Wire
- Floating cable
- LC to LC Fiber Patch Cables
- Flexible Cable
- Drag Chain Cables
- Silicone Rubber Low Temperature Resistant Cable
- All-Aluminum Conductors for Overhead Power Lines
- Aerial Bundled Cable (ABC Cable)
- Aerial Insulation Line (AIL)
- Bare Stranded Conductors
- Wind Farm Cables
- Overhead Service Drop Cable
- Concentric Service Cable
- Telephone Drop Cable
- Solar PV Cable
Recent Posts