Understanding Computer Monitor Cable Types
computer monitor cable types
Computer monitor cable types play a crucial role in determining your display quality, refresh rates, and overall viewing experience. With numerous connection standards available, choosing the right monitor cable can significantly impact your productivity, gaming performance, and multimedia consumption. This comprehensive guide explores all major computer monitor cable types, their capabilities, and ideal use cases.
Modern displays support various connection standards, each with unique advantages and limitations. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions when setting up single or multiple monitor configurations, ensuring optimal performance for your specific needs.
HDMI Cables - The Universal Standard
HDMI Overview
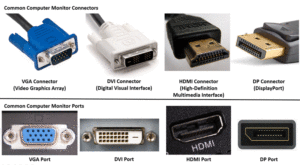
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) represents the most widely adopted computer monitor cable type in modern setups. HDMI cables transmit both video and audio signals through a single connection, making them ideal for home offices and entertainment systems.
HDMI Versions and Capabilities
HDMI 1.4: Supports 4K resolution at 30Hz, 1080p at 120Hz, and includes 3D video support. This version remains common in older monitors and budget displays.
HDMI 2.0: Delivers 4K resolution at 60Hz, supports HDR (High Dynamic Range), and offers increased bandwidth up to 18 Gbps. Most modern monitors feature HDMI 2.0 ports.
HDMI 2.1: The latest standard supports 8K at 60Hz, 4K at 120Hz, Variable Refresh Rate (VRR), and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM). Gaming monitors increasingly adopt HDMI 2.1 for high refresh rate gaming.
HDMI Use Cases
HDMI cables excel in multimedia applications, console gaming, and general computing tasks. They're perfect for connecting laptops to external monitors, setting up dual-screen workstations, and creating home theater PC configurations.
DisplayPort - The Professional Choice
DisplayPort Advantages
DisplayPort cables offer superior performance for professional applications and high-end gaming setups. Unlike HDMI, DisplayPort was designed specifically for computer displays, providing advanced features like daisy-chaining multiple monitors.
DisplayPort Versions
DisplayPort 1.2: Supports 4K at 60Hz, 1440p at 165Hz, and enables multi-stream transport for daisy-chaining up to four displays.
DisplayPort 1.4: Adds HDR support, Display Stream Compression (DSC), and improved 4K performance. This version handles 8K at 60Hz with compression.
DisplayPort 2.0: Delivers unprecedented bandwidth up to 80 Gbps, supporting 8K at 120Hz, dual 4K at 120Hz, and enhanced VRR capabilities.
DisplayPort Use Cases
DisplayPort excels in professional graphics work, competitive gaming, and multi-monitor setups. Content creators, gamers seeking high refresh rates, and professionals requiring color accuracy prefer DisplayPort connections.
USB-C and Thunderbolt - The Modern Solution
USB-C Display Connectivity
USB-C has revolutionized computer monitor cable types by combining power delivery, data transfer, and video output in a single reversible connector. Many modern laptops rely exclusively on USB-C for external display connections.
USB-C Capabilities
USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode: Delivers 4K at 60Hz while simultaneously charging laptops up to 100W. This makes USB-C ideal for clean, minimal desktop setups.
Thunderbolt 3/4: Provides exceptional bandwidth up to 40 Gbps, supporting dual 4K displays, 8K single displays, and daisy-chaining up to six devices.
USB-C Advantages
USB-C monitor cables simplify connectivity by reducing cable clutter, providing laptop charging, and enabling single-cable docking solutions. They're perfect for ultrabooks, MacBooks, and modern workstations.
Legacy Cable Types - Still Relevant
VGA Cables
Video Graphics Array (VGA) represents the oldest computer monitor cable type still in use. VGA transmits analog signals and supports resolutions up to 1920x1200, though image quality degrades at higher resolutions and longer cable lengths.
VGA Use Cases: Legacy system support, projector connections, and budget setups where digital cables aren't available.
DVI Cables
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) bridges the gap between analog VGA and modern digital standards. DVI comes in three variants:
DVI-D (Digital): Supports resolutions up to 2560x1600 at 60Hz with dual-link connections.
DVI-I (Integrated): Combines digital and analog signals, offering backward compatibility with VGA adapters.
DVI-A (Analog): Rarely used analog-only variant primarily for legacy compatibility.
When to Use Legacy Cables
Legacy computer monitor cable types remain useful for older systems, budget builds, and specific industrial applications where newer standards aren't supported.
Choosing the Right Monitor Cable Type
Resolution and Refresh Rate Requirements
Your monitor's native resolution and desired refresh rate determine the minimum cable standard required:
1080p Gaming: HDMI 1.4, DisplayPort 1.2, or USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode all provide adequate performance.
1440p High Refresh: DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 minimum, with DisplayPort 1.4 preferred for 165Hz+ gaming.
4K Professional Work: HDMI 2.0 or DisplayPort 1.4 minimum, with DisplayPort 2.0 ideal for future-proofing.
8K Content Creation: DisplayPort 2.0 or HDMI 2.1 required for optimal performance.
Device Compatibility Considerations
Check your graphics card and monitor ports before selecting computer monitor cable types. Many modern laptops only offer USB-C ports, requiring adapters or USB-C native cables.
Graphics Cards: High-end GPUs typically include multiple DisplayPort outputs and one or two HDMI ports.
Laptops: Business laptops often feature USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode, while gaming laptops may include HDMI and mini-DisplayPort.
Monitors: Professional monitors emphasize DisplayPort connectivity, while consumer displays prioritize HDMI compatibility.
Multi-Monitor Setup Considerations
Daisy-Chaining with DisplayPort
DisplayPort's Multi-Stream Transport (MST) enables daisy-chaining multiple monitors through a single connection. This reduces cable clutter and simplifies ultra-wide or multi-display configurations.
Requirements: Graphics card with DisplayPort 1.2+, monitors with DisplayPort MST support, and adequate bandwidth for all connected displays.
Limitations: Total bandwidth is shared among all daisy-chained displays, potentially limiting individual monitor refresh rates.
Mixed Cable Configurations
Many users combine different computer monitor cable types within single setups. For example, using DisplayPort for a primary gaming monitor while connecting secondary displays via HDMI.
Bandwidth Management
High-resolution multi-monitor setups require careful bandwidth planning. Multiple 4K displays may exceed single-cable capabilities, necessitating separate connections or display compression.
Cable Quality and Length Considerations
Active vs. Passive Cables
Passive Cables: Standard cables without signal amplification, suitable for lengths up to 6 feet for 4K signals and 15 feet for 1080p.
Active Cables: Include signal boosters enabling longer runs while maintaining signal integrity. Essential for distances exceeding passive cable limits.
Cable Construction Quality
Premium computer monitor cable types feature better shielding, gold-plated connectors, and higher-quality conductors. These improvements reduce electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable signal transmission.
Length Limitations
Different cable types have varying length restrictions:
HDMI: Up to 25 feet for 1080p, 15 feet for 4K without active amplification.
DisplayPort: Similar limitations to HDMI, with active cables extending usable lengths.
USB-C: Generally limited to 6 feet for full-bandwidth applications.
Gaming-Specific Considerations
Refresh Rate and Response Time
Competitive gamers prioritize high refresh rates and low input lag. DisplayPort 1.4 and HDMI 2.1 support high refresh rate gaming at 1440p and 4K resolutions.
Variable Refresh Rate Technologies
G-Sync: NVIDIA's proprietary technology works over DisplayPort and select HDMI 2.1 implementations.
FreeSync: AMD's open standard supports both DisplayPort and HDMI connections.
HDMI VRR: Part of HDMI 2.1 specification, providing variable refresh rate support for gaming consoles and compatible displays.
Console Gaming Cable Requirements
PlayStation 5: HDMI 2.1 required for 4K at 120Hz gaming and VRR support.
Xbox Series X/S: Similar HDMI 2.1 requirements for optimal gaming performance.
Nintendo Switch: HDMI 1.4 adequate for dock connectivity and 1080p output.
Professional and Creative Applications
Color Accuracy Requirements
Professional content creators require accurate color reproduction and wide color gamuts. DisplayPort typically offers superior color support compared to HDMI.
HDR Support
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content requires compatible computer monitor cable types:
HDR10: Supported by HDMI 2.0a+ and DisplayPort 1.4+.
Dolby Vision: Requires HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 1.4 with specific monitor support.
Calibration Considerations
Professional monitors often include hardware calibration features accessible through DisplayPort connections, enabling precise color management for photography and video editing.
Troubleshooting Common Cable Issues
No Signal Problems
Check Connections: Ensure cables are firmly seated and compatible with both devices.
Try Different Ports: Test alternative ports on both graphics cards and monitors.
Update Drivers: Ensure graphics drivers support the desired resolution and refresh rate.
Image Quality Issues
Bandwidth Limitations: Reduce refresh rates or resolution if experiencing artifacts or flickering.
Cable Quality: Replace low-quality cables that may cause signal degradation.
Interference: Route cables away from power lines and wireless devices.
Intermittent Connection Problems
Loose Connectors: Check for worn or damaged connectors requiring replacement.
Cable Fatigue: Replace cables showing wear from repeated bending or stress.
Port Wear: Consider using different ports if specific connections become unreliable.
Future-Proofing Your Setup
Emerging Standards
DisplayPort 2.1: Currently in development, promising even higher bandwidth and improved features.
HDMI 2.2: Expected to enhance gaming features and support higher resolutions.
USB4: Next-generation USB-C with improved display capabilities and universal compatibility.
Investment Considerations
When selecting computer monitor cable types, consider your upgrade timeline and performance requirements. Investing in higher-specification cables often provides better long-term value.
Backwards Compatibility
Most modern cable standards maintain backwards compatibility, ensuring new cables work with older devices while providing upgrade paths for future hardware.
Conclusion
Understanding computer monitor cable types empowers you to make informed decisions for optimal display performance. HDMI cables offer universal compatibility and multimedia features, DisplayPort provides professional-grade performance and advanced features, while USB-C delivers modern convenience and versatility.
Your specific needs determine the ideal cable choice. Gamers benefit from DisplayPort's high refresh rate support, professionals appreciate color accuracy and multi-monitor capabilities, while general users find HDMI's simplicity and widespread compatibility appealing.
Consider your current hardware, performance requirements, and future upgrade plans when selecting monitor cables. Quality cables represent worthwhile investments that ensure reliable connections and optimal performance across your computing experience.
Whether building a new system, upgrading existing displays, or troubleshooting connection issues, this guide provides the knowledge needed to select appropriate computer monitor cable types for any application. Remember that the best cable choice balances current needs with future expansion possibilities, ensuring your display setup remains capable and relevant as technology evolves.