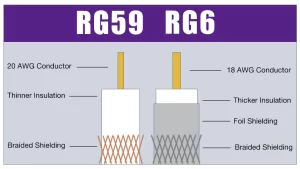
When setting up cable TV, internet, or security camera systems, choosing the right coaxial cable can make a significant difference in signal quality and performance. Two of the most common types you'll encounter are RG59 and RG6 cables. Understanding their differences will help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
difference between rg59 and rg6
What Are RG59 and RG6 Coaxial Cables?
Both RG59 and RG6 are types of coaxial cables used to transmit radio frequency signals. The 'RG' stands for 'Radio Guide,' a military specification system that dates back to World War II. These cables consist of a center conductor, insulation, shielding, and an outer jacket.
Key Differences Between RG59 and RG6
Physical Construction
- Thinner overall diameter (approximately 0.242 inches)
- 20 AWG center conductor (thinner)
- Less shielding
- More flexible and easier to bend
- Thicker overall diameter (approximately 0.332 inches)
- 18 AWG center conductor (thicker)
- Better shielding with quad-shield options
- More rigid but provides superior performance
Frequency Range and Bandwidth
The most critical difference lies in their frequency handling capabilities:
RG59:
- Effective frequency range: Up to 1 GHz
- Suitable for basic cable TV and analog applications
- Limited bandwidth capacity
RG6:
- Effective frequency range: Up to 3 GHz
- Supports high-definition signals and digital applications
- Greater bandwidth for modern requirements
Signal Loss and Attenuation
Signal loss is measured in decibels (dB) per 100 feet:
RG59 Signal Loss:
- Higher attenuation rates
- Significant signal degradation over long distances
- Best for runs under 150 feet
RG6 Signal Loss:
- Lower attenuation rates
- Maintains signal integrity over longer distances
- Suitable for runs up to 300+ feet
When to Use RG59 vs RG6
Choose RG59 When:
- Installing short-distance analog security cameras
- Connecting older cable TV equipment
- Budget is a primary concern
- Working in tight spaces requiring flexibility
- Dealing with legacy systems that specifically require RG59
Choose RG6 When:
- Installing satellite TV systems (DirecTV, Dish Network)
- Setting up high-definition cable TV
- Running cables over long distances
- Installing modern security camera systems
- Future-proofing your installation
- Connecting internet modems and routers
Performance Comparison
| Feature | RG59 | RG6 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Frequency | 1 GHz | 3 GHz |
| Signal Loss (100ft at 1000MHz) | ~6.5 dB | ~4.3 dB |
| Recommended Distance | Up to 150 feet | Up to 300+ feet |
| HD Signal Support | Limited | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Installation Difficulty | Easier (more flexible) | Moderate (less flexible) |
Common Applications
RG59 Applications:
- Analog CCTV systems
- Short-run cable TV connections
- Composite video transmission
- RF testing equipment connections
- Amateur radio applications
RG6 Applications:
- Satellite television installations
- Cable internet connections
- HD cable TV systems
- IP security cameras
- Antenna connections for over-the-air TV
Installation Considerations
Tools and Connectors
Both cables require specific tools and connectors:
- RG59: Uses smaller F-connectors and BNC connectors
- RG6: Uses larger F-connectors designed for the thicker cable
Environmental Factors
Consider these factors when choosing:
- Outdoor installations: RG6 with weatherproof jacket
- Underground burial: Direct burial rated cables
- Indoor use: Standard PVC jacket sufficient
- Plenum spaces: Fire-rated plenum cables required
Cost Analysis
While RG59 is initially cheaper, consider the total cost of ownership:
RG59 Costs:
- Lower upfront cable cost
- Potential signal boosters needed for long runs
- Possible replacement costs for inadequate performance
RG6 Costs:
- Higher upfront cable cost
- Better long-term value
- Reduced need for signal amplification
- Future-proof investment
Future-Proofing Your Installation
Technology continues to evolve, and signal requirements increase over time. RG6 cable provides:
- Support for 4K and 8K video signals
- Compatibility with emerging broadcast standards
- Reduced need for system upgrades
- Better return on investment
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Poor Signal Quality:
- Check cable type matches application requirements
- Verify proper connector installation
- Test for signal loss over cable length
- Consider upgrading from RG59 to RG6
Installation Problems:
- Use appropriate tools for cable type
- Ensure proper grounding
- Avoid sharp bends that damage the cable
- Use weatherproof connectors for outdoor applications
Professional Installation vs DIY
While both cables can be installed by homeowners, consider professional installation for:
- Complex multi-room systems
- Outdoor and underground runs
- Commercial applications
- Systems requiring signal analysis and optimization
Conclusion
The choice between RG59 and RG6 coaxial cable depends on your specific application, distance requirements, and budget. For most modern installations, RG6 is the recommended choice due to its superior performance, future-proofing capabilities, and support for high-definition signals.
RG59 remains suitable for specific applications like short-run analog security cameras or budget-conscious installations with minimal signal requirements. However, the relatively small price difference between the two makes RG6 the smarter long-term investment for most users.
When in doubt, choose RG6 for new installations to ensure compatibility with current and future technology requirements. The improved signal quality and reduced maintenance issues typically justify the slightly higher initial cost.
Remember to always use quality connectors, proper installation techniques, and consider environmental factors when planning your coaxial cable installation. Whether you choose RG59 or RG6, proper installation is crucial for optimal performance.