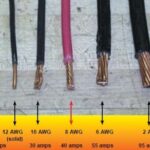
When it comes to electrical wiring, copper and aluminum are the two most common conductor materials used in power distribution, construction, and industrial systems.
While both metals conduct electricity effectively, they differ in performance, weight, cost, and installation requirements.

Differences between copper and aluminum wire
Understanding the differences between copper and aluminum wire is essential to choosing the right material for your project — whether it’s residential wiring, industrial cable, or power transmission.
1. Conductivity and Electrical Performance
Copper wire has a higher electrical conductivity than aluminum — approximately 61% of the International Annealed Copper Standard (IACS) versus 39% for aluminum.
👉 What this means:
Copper can carry more current through a smaller cross-sectional area.
Aluminum wires must be larger in diameter to deliver the same power load.
Copper wiring provides lower voltage drop and better energy efficiency.
✅ Winner: Copper wire offers superior conductivity and electrical performance.
2. Strength and Durability
Copper is mechanically stronger and less prone to creep (permanent deformation under long-term stress).
Aluminum, being softer, may loosen over time at connection points — a key consideration in electrical safety.
👉 Result:
Copper connections are more stable and require less maintenance.
Aluminum requires special lugs and anti-oxidant compounds to prevent loosening or corrosion.
✅ Winner: Copper wire for mechanical strength and reliability.
3. Weight and Flexibility
Aluminum is about one-third the weight of copper, making it easier to handle and install, especially in large-scale power transmission cables.
👉 Result:
Aluminum wire is ideal for overhead power lines or long-distance transmission.
Copper wire is better for tight spaces and flexible installations, such as in buildings and equipment.
✅ Winner: Aluminum for lightweight applications; Copper for compact wiring systems.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Copper naturally resists oxidation and corrosion. Aluminum forms an oxide layer that can increase resistance at connections, leading to potential overheating or failure if not properly treated.
👉 Result:
Copper is self-protective and stable.
Aluminum requires special anti-oxidant grease and approved connectors.
✅ Winner: Copper for better corrosion resistance and safety.
5. Cost and Availability
Aluminum wire is significantly cheaper than copper — often 30–50% lower in cost depending on market prices.
That’s why aluminum is commonly used for utility, industrial, and large feeder applications, where cost efficiency is critical.
✅ Winner: Aluminum wire for budget-sensitive, large-scale installations.
6. Applications Comparison
| Application Type | Preferred Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Residential wiring | Copper | Safety, reliability, compact size |
| Power transmission | Aluminum | Lightweight, cost-effective for long distances |
| Industrial power cables | Copper | Better conductivity and mechanical strength |
| Temporary power or feeders | Aluminum | Lightweight and affordable |
| Electronics / control wires | Copper | High conductivity and signal integrity |
7. Safety Considerations
Older aluminum wiring (especially in homes built before 1980) has been linked to connection failures and fire risks due to improper terminations.
Modern aluminum conductors are much safer when installed correctly using Al/Cu rated connectors and anti-oxidant compounds.
Copper, on the other hand, has excellent long-term stability, making it a safer option for critical or high-load systems.
8. Environmental and Energy Impact
Although copper is more efficient, its extraction and refining process is more energy-intensive.
Aluminum is lighter and easier to recycle, making it a more sustainable option for large-scale applications when used properly.
Summary: Copper vs Aluminum Wire
| Property | Copper Wire | Aluminum Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Excellent | Good |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Strength | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Fair (needs treatment) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Residential, industrial, electronics | Transmission, feeders, utility |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate (requires checks) |
Conclusion
Both copper and aluminum wires have their advantages.
Copper excels in conductivity, durability, and safety, making it ideal for residential and industrial wiring.
Aluminum provides a lighter and more economical solution for large-scale or overhead installations.
The right choice depends on your budget, installation environment, and performance requirements.
👉 Looking for high-quality copper or aluminum wire?
Contact TOT Wire & Cable today for expert guidance and competitive pricing on copper conductors, aluminum power cables, and custom wiring solutions for your project.