When planning an electrical installation, one common question is whether to use metal clad cable (MC cable) or conduit wiring. Both methods protect electrical conductors, but they differ in construction, applications, installation practices, and cost. If you’re trying to decide between metal clad cable vs conduit, this guide will help you understand which option is best for your project.
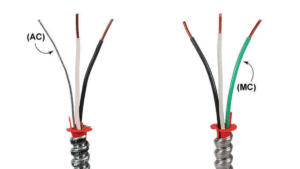
metal clad cable vs conduit
What Is Metal Clad (MC) Cable?
MC cable is a type of electrical cable with:
Insulated conductors inside
A flexible metal armor (typically aluminum or steel) that serves as protection
An included grounding conductor
Typical Uses of MC Cable:
Indoor branch circuits and feeders
Commercial buildings, hospitals, and industrial plants
Exposed runs in ceilings, walls, or mechanical rooms
Applications requiring quick installation without running conduit
What Is Conduit Wiring?
Conduit is a protective tubing system through which electrical wires are pulled. Conduits can be:
Metal (EMT, IMC, RMC) – durable, fire-resistant, often required in commercial settings
Nonmetallic (PVC, ENT, HDPE) – lightweight, corrosion-resistant, used in wet or underground applications
Typical Uses of Conduit:
Exposed wiring in commercial and industrial facilities
Outdoor and underground runs
Environments where wiring needs extra mechanical or fire protection
Situations requiring frequent rewiring or upgrades
Metal Clad Cable vs. Conduit: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | MC Cable (Metal Clad) | Conduit Wiring |
|---|---|---|
| Protection | Flexible metal armor provides built-in protection | Requires conduit tubing plus separate wires |
| Installation Speed | Faster – cable is pre-assembled | Slower – wires must be pulled into conduit |
| Flexibility | Easier to bend and route through tight spaces | Requires bending tools and fittings |
| Grounding | Includes grounding conductor | Ground path depends on conduit type/wire |
| Durability | Strong, but less than rigid conduit | Rigid conduit offers maximum durability |
| Rewiring/Upgrades | Difficult once installed | Easier to pull new wires through conduit |
| Cost | Lower overall labor cost | Higher material and labor costs |
| Applications | Commercial interiors, feeders, branch circuits | Harsh environments, outdoors, underground |
Advantages and Disadvantages
MC Cable Advantages:
Faster, simpler installation
Lower labor costs compared to conduit
Flexible for routing in ceilings and walls
Code-approved for many commercial and industrial applications
MC Cable Disadvantages:
Harder to rewire or upgrade later
Less durable than rigid conduit in extreme conditions
Not always suitable for outdoor or underground use
Conduit Advantages:
Provides the highest level of protection against impact, fire, and moisture
Makes rewiring and future expansion easier
Required by code in many commercial, industrial, or outdoor applications
Conduit Disadvantages:
Higher cost for both materials and labor
Installation is slower and requires more skill
Less flexible in tight spaces compared to MC cable
Which Should You Use?
Choose MC cable if you need a cost-effective, code-compliant solution for indoor branch circuits and feeders, especially in commercial interiors.
Choose conduit wiring if you’re working outdoors, underground, or in environments with high moisture, mechanical damage risk, or frequent wiring changes.
Conclusion
When comparing metal clad cable vs conduit wiring, the decision depends on your project’s environment, budget, and code requirements. MC cable offers faster, more economical installation for most indoor applications, while conduit provides unmatched protection and flexibility for harsh or outdoor environments.
👉 Always check local NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements before installation and consult with a licensed electrician to ensure safety and compliance.




1 comment
Vorbelutr ioperbir 10/03/2025
I'm still learning from you, while I'm trying to reach my goals. I certainly liked reading all that is written on your website.Keep the stories coming. I enjoyed it!