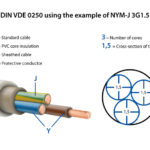
What is Mining Cable?
Mining cable is a specialized type of heavy-duty electrical cable specifically engineered for the harsh conditions found in underground mining operations and surface mining facilities. These industrial-grade cables are designed to withstand extreme mechanical stress, chemical exposure, moisture, and temperature variations while maintaining reliable power transmission and safety in mining environments.
Underground mining cables must meet stringent safety standards and regulatory requirements to ensure worker safety and operational continuity in some of the world's most challenging industrial environments. From coal mines to metal ore extraction facilities, mining cables form the electrical backbone of modern mining operations.
Mining Cable Construction and Design
Heavy-Duty Conductor Design
Mining cables feature robust copper or aluminum conductors designed to handle high current loads typical in mining equipment. The conductor construction includes:
Stranded Copper Conductors: Multiple wire strands provide flexibility while maintaining excellent conductivity for mining machinery and equipment power supply.
Aluminum Conductors: Used in larger mining cables where weight reduction is important, particularly for portable mining equipment and overhead installations.
Conductor Shielding: Many mining cables include conductor shielding to prevent electrical interference and ensure stable power delivery to sensitive mining control systems.
Mining-Grade Insulation
The insulation system in mining cables must withstand harsh underground conditions:
EPDM Rubber Insulation: Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer rubber provides excellent resistance to ozone, chemicals, and temperature extremes common in mining environments.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Offers superior electrical properties and moisture resistance for permanent mining installations.
EPR Insulation: Ethylene Propylene Rubber insulation combines flexibility with chemical resistance for portable mining equipment cables.
Protective Armoring and Jacketing
Mining cable protection systems include multiple layers:
Steel Wire Armor: Galvanized steel wire armor provides mechanical protection against crushing, impact, and rodent damage in underground mining tunnels.
Interlocked Armor: Metal tape or wire interlocked armor offers flexibility while maintaining protection for mining cables subject to movement.
Mining-Grade Jackets: Specialized outer jackets resist oils, acids, alkalis, and abrasion encountered in mining operations.
Types of Mining Cables
Portable Mining Cable
Portable mining cables are designed for mobile mining equipment including:
- Continuous miners
- Shuttle cars
- Roof bolters
- Mining locomotives
- Portable ventilation equipment
These flexible mining cables feature extra-flexible construction and enhanced abrasion resistance to withstand constant movement and harsh handling.
Stationary Mining Cable
Fixed installation mining cables serve permanent mining infrastructure:
- Main power distribution systems
- Conveyor belt motors
- Pumping stations
- Ventilation systems
- Lighting circuits
Trailing Cable
Mining trailing cables connect mobile equipment to power sources, featuring:
- High flexibility for equipment movement
- Enhanced strain relief at connections
- Superior abrasion and cut resistance
- Chemical resistance to mining fluids
Control and Instrumentation Cable
Mining control cables serve critical functions:
- Mining equipment control systems
- Safety monitoring equipment
- Communication systems
- Data transmission networks
- Emergency systems
Mining Cable Standards and Certifications
MSHA Approval
The Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) requires approval for all electrical equipment used in underground coal mines. MSHA-approved mining cables meet strict flame resistance and safety requirements.
IEEE Mining Standards
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers standards, particularly IEEE 525, specify requirements for mining cables used in hazardous locations and underground installations.
IEC Mining Cable Standards
International Electrotechnical Commission standards, including IEC 60092 series, provide global specifications for mining cable construction and performance.
CSA Mining Certifications
Canadian Standards Association certifications ensure mining cables meet North American safety and performance requirements for mining applications.
ATEX Compliance
For mining operations in potentially explosive atmospheres, ATEX-compliant mining cables provide additional safety assurance against ignition sources.
Applications of Mining Cables
Underground Coal Mining
Coal mining operations require specialized cables for:
- Longwall mining equipment
- Room and pillar mining machinery
- Coal preparation plants
- Underground transportation systems
- Mine ventilation and safety systems
Hard Rock Mining
Metal ore mining applications include:
- Continuous miners and development equipment
- Ore processing machinery
- Underground crushing and conveying systems
- Mine dewatering pumps
- Shaft hoisting equipment
Surface Mining Operations
Open-pit and surface mining use mining cables for:
- Large excavation equipment
- Haul truck charging stations
- Processing plant equipment
- Crushing and screening machinery
- Conveyor belt systems
Mining Support Systems
Critical mining infrastructure requiring specialized cables:
- Mine ventilation systems
- Emergency communication networks
- Lighting and power distribution
- Safety monitoring equipment
- Fire suppression systems
Environmental Challenges in Mining
Chemical Exposure
Mining cables must resist exposure to:
- Acidic mine water
- Petroleum-based hydraulic fluids
- Industrial solvents and cleaners
- Salt solutions and brines
- Corrosive gases and vapors
Physical Hazards
Underground mining presents unique physical challenges:
- Rock falls and cave-ins
- Equipment impact and crushing forces
- Sharp rock surfaces and abrasion
- Constant vibration from machinery
- Temperature fluctuations
Moisture and Water
Mining operations involve significant moisture exposure:
- High humidity in underground environments
- Standing water and flooding
- Steam and condensation
- Pressure washing and cleaning operations
- Groundwater infiltration
Installation Considerations for Mining Cables
Cable Support Systems
Proper support prevents cable damage and ensures safety:
- Heavy-duty cable trays designed for mining environments
- Festoon systems for mobile equipment
- Cable reels and take-up systems
- Anchor points and strain relief
- Protection against mechanical damage
Routing and Protection
Strategic cable routing minimizes hazards:
- Avoiding high-traffic areas where possible
- Protection from falling objects
- Separation from heat sources
- Adequate clearance from moving equipment
- Emergency egress considerations
Termination and Connections
Mining cable connections require special attention:
- Explosion-proof junction boxes
- Waterproof and corrosion-resistant terminals
- Proper grounding and bonding
- Strain relief at all connection points
- Regular inspection and maintenance access
Safety Requirements and Regulations
Electrical Safety Standards
Mining electrical safety encompasses:
- Ground fault protection systems
- Arc fault circuit interruption
- Proper grounding and bonding
- Electrical equipment spacing requirements
- Lockout/tagout procedures for maintenance
Fire Safety Considerations
Mining cable fire safety includes:
- Flame-resistant cable construction
- Low smoke emission requirements
- Fire detection and suppression systems
- Emergency evacuation procedures
- Proper cable separation and barriers
Hazardous Location Classifications
Mining environments often qualify as hazardous locations requiring:
- Intrinsically safe equipment and cables
- Explosion-proof enclosures
- Proper area classification assessment
- Specialized installation techniques
- Regular safety inspections and testing
Mining Cable Maintenance and Testing
Routine Inspection Programs
Regular inspection prevents failures and ensures safety:
- Visual inspection for physical damage
- Thermal imaging for hot spots
- Insulation resistance testing
- Ground fault testing
- Mechanical integrity assessment
Predictive Maintenance
Advanced maintenance techniques include:
- Partial discharge testing
- Time domain reflectometry
- Infrared thermography
- Vibration analysis of cable support systems
- Trending of electrical parameters
Emergency Response
Mining operations require rapid response to cable failures:
- Emergency repair procedures
- Backup power systems
- Spare cable inventory management
- Rapid deployment techniques
- Safety protocols during repairs
Selection Criteria for Mining Cables
Electrical Requirements
Proper cable selection considers:
- Voltage and current ratings
- Power factor and harmonic considerations
- Starting current requirements for large motors
- Voltage drop limitations
- System grounding requirements
Environmental Factors
Environmental assessment includes:
- Temperature extremes and variations
- Chemical exposure potential
- Moisture and water exposure
- Mechanical stress and movement
- UV exposure for surface installations
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance requirements encompass:
- Local mining authority regulations
- International safety standards
- Environmental protection requirements
- Worker safety regulations
- Insurance and liability considerations
Advanced Mining Cable Technologies
Smart Cable Systems
Modern mining cables may incorporate:
- Integrated monitoring systems
- Temperature and strain sensors
- Fault location capabilities
- Wireless communication features
- Predictive maintenance alerts
Enhanced Materials
Ongoing development focuses on:
- Improved insulation compounds
- Advanced armor materials
- Lightweight conductor alternatives
- Enhanced flame resistance
- Reduced environmental impact
Digital Integration
Integration with mining automation includes:
- Power line communication capabilities
- Ethernet over power systems
- Fiber optic integration
- Remote monitoring and control
- Data analytics and optimization
Cost Considerations and Economics
Initial Investment
Mining cable costs include:
- Premium materials and construction
- Specialized testing and certification
- Installation in challenging environments
- Support infrastructure requirements
- Compliance and documentation costs
Operational Benefits
Economic advantages of quality mining cables:
- Reduced downtime and maintenance
- Improved safety and lower insurance costs
- Extended service life
- Better system reliability
- Compliance with regulations
Total Cost of Ownership
Long-term cost analysis considers:
- Installation and commissioning costs
- Maintenance and inspection expenses
- Replacement frequency
- Downtime costs from failures
- Safety incident prevention value
Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Recycling and Disposal
Responsible mining cable management includes:
- Copper and aluminum recovery programs
- Proper disposal of insulation materials
- Minimizing landfill waste
- Hazardous material handling
- Environmental impact assessment
Sustainable Manufacturing
Modern mining cable production emphasizes:
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Recyclable materials where possible
- Energy-efficient manufacturing processes
- Responsible sourcing of raw materials
- Compliance with environmental regulations
Future Trends in Mining Cables
Automation Integration
Mining industry automation drives demand for:
- Higher data transmission capabilities
- Integrated power and communication cables
- Wireless power transmission research
- Automated cable handling systems
- Remote operation capabilities
Safety Innovations
Advancing safety technology includes:
- Real-time cable health monitoring
- Automatic fault detection systems
- Enhanced fire detection and suppression
- Improved worker protection systems
- Emergency response automation
Sustainability Focus
Environmental considerations drive:
- Reduced material usage
- Improved recyclability
- Lower environmental impact materials
- Energy-efficient designs
- Lifecycle assessment integration
Troubleshooting Common Mining Cable Issues
Insulation Failures
Common causes and solutions:
- Moisture ingress prevention and detection
- Chemical resistance assessment and upgrades
- Temperature monitoring and management
- Physical protection improvements
- Regular testing and maintenance
Mechanical Damage
Prevention and mitigation strategies:
- Improved cable routing and protection
- Enhanced support systems
- Training on proper handling procedures
- Regular inspection programs
- Prompt repair of minor damage
Connection Problems
Addressing connection issues:
- Proper termination techniques
- Corrosion prevention measures
- Strain relief improvements
- Environmental protection upgrades
- Regular maintenance schedules
Conclusion
Mining cables represent a critical component of safe and efficient mining operations worldwide. Their specialized construction and rigorous testing ensure reliable power distribution in some of the most challenging industrial environments on Earth. From underground coal mines to surface metal extraction facilities, these heavy-duty cables provide the electrical infrastructure necessary for modern mining operations.
When selecting mining cables, careful consideration of environmental conditions, regulatory requirements, and operational demands ensures optimal performance and safety. Proper installation, maintenance, and monitoring maximize cable service life while minimizing risks to personnel and equipment.
The continued evolution of mining cable technology, driven by automation, safety requirements, and environmental considerations, promises even better performance and reliability for future mining operations. Investment in quality mining cables and proper electrical infrastructure remains essential for safe, efficient, and profitable mining operations in the 21st century.