What is Rubberised Cable?
Rubberised cable, also known as rubber sheathed cable or rubber insulated cable, is a flexible electrical cable featuring rubber-based insulation and jacketing materials. These versatile cables are designed to provide superior flexibility, durability, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for portable applications, industrial equipment, and demanding electrical installations.
The rubber construction of these cables offers exceptional performance in applications requiring frequent flexing, exposure to oils and chemicals, temperature extremes, and outdoor weather conditions. From construction sites to manufacturing facilities, rubberised cables deliver reliable power transmission where standard PVC cables would fail.
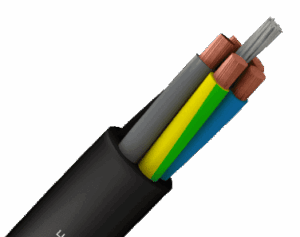
Rubberised Cable
Rubberised Cable Construction
Rubber Insulation Types
Modern rubberised cables utilize various rubber compounds optimized for specific applications:
EPDM Rubber (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Provides excellent weather resistance, ozone protection, and temperature stability. EPDM insulated cables are ideal for outdoor applications and harsh environmental conditions.
EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber): Offers superior electrical properties with good flexibility and chemical resistance. EPR rubber cables are commonly used in industrial and commercial applications.
Natural Rubber: Traditional rubber insulation providing excellent flexibility and electrical properties, though with limited chemical and weather resistance compared to synthetic alternatives.
Neoprene Rubber: Chloroprene rubber offers balanced performance with good oil resistance, flame retardancy, and mechanical durability for general-purpose applications.
Silicone Rubber: High-temperature rubber insulation capable of operating at extreme temperatures while maintaining flexibility and electrical integrity.
Conductor Materials
Rubberised cables feature various conductor options:
Stranded Copper Conductors: Provide excellent conductivity and flexibility for most rubber cable applications. Fine stranding enhances cable flexibility for portable applications.
Tinned Copper Conductors: Tin-plated copper offers enhanced corrosion resistance in harsh environments while maintaining excellent electrical properties.
Aluminum Conductors: Used in larger rubber cables where weight reduction is important, particularly for overhead installations and portable equipment.
Protective Sheathing
The outer sheath of rubberised cables provides environmental protection:
Heavy Duty Rubber Sheath: Multi-layer rubber construction offers maximum protection against mechanical damage, chemicals, and environmental factors.
Oil Resistant Sheath: Specialized rubber compounds resist petroleum products, hydraulic fluids, and industrial oils common in equipment applications.
Flame Retardant Sheath: Fire-resistant rubber formulations meet safety requirements for indoor installations and hazardous locations.
Types of Rubberised Cables
Flexible Rubber Cable
Flexible rubber cables are designed for applications requiring frequent movement:
- Portable tools and equipment
- Construction site wiring
- Temporary power installations
- Mobile machinery connections
- Entertainment and event lighting
These extra flexible cables feature fine-stranded conductors and soft rubber insulation optimized for repeated flexing without fatigue.
Heavy Duty Rubber Cable
Industrial-grade rubber cables built for demanding applications:
- Manufacturing equipment
- Mining machinery
- Marine installations
- Outdoor industrial systems
- Heavy construction equipment
Heavy duty construction includes reinforced insulation, armored protection options, and enhanced environmental resistance.
Welding Cable
Specialized rubber cables for welding applications:
- Arc welding equipment
- Resistance welding systems
- Plasma cutting equipment
- Industrial welding installations
- Portable welding operations
Welding cables feature extra-flexible construction with superior heat resistance and electrical performance for high-current applications.
Submersible Rubber Cable
Water-resistant cables for underwater and wet applications:
- Submersible pumps
- Underwater lighting
- Marine equipment
- Irrigation systems
- Water treatment facilities
These cables incorporate waterproof construction with specialized rubber compounds resistant to water absorption and degradation.
High Temperature Rubber Cable
Heat-resistant cables for extreme temperature applications:
- Industrial furnaces and ovens
- Heat treatment equipment
- Power generation facilities
- Chemical processing plants
- Automotive applications
High-temperature rubber insulation maintains flexibility and electrical integrity at elevated temperatures where standard cables would fail.
Applications of Rubberised Cables
Industrial Applications
Manufacturing and industrial facilities rely on rubber cables for:
- Motor connections requiring flexibility
- Portable equipment and tools
- Conveyors and material handling systems
- Process equipment with movement
- Emergency and backup power systems
Construction and Building
Construction sites use rubberised cables for:
- Temporary power distribution
- Portable tools and equipment
- Site lighting systems
- Concrete pumping equipment
- Tower cranes and lifting equipment
Marine and Offshore
Marine environments benefit from rubber cable properties:
- Boat and yacht electrical systems
- Offshore platform equipment
- Marine winches and deck machinery
- Underwater installations
- Port and harbor facilities
Entertainment and Events
Portable entertainment requires flexible cables:
- Stage and concert lighting
- Sound system connections
- Portable power distribution
- Temporary event installations
- Mobile broadcasting equipment
Agricultural Applications
Farm and agricultural equipment uses rubber cables for:
- Irrigation control systems
- Livestock facility equipment
- Mobile agricultural machinery
- Grain handling equipment
- Greenhouse installations
Advantages of Rubberised Cables
Superior Flexibility
The primary advantage of rubber insulated cables lies in their exceptional flexibility. Unlike rigid PVC cables, rubber cables maintain flexibility even in cold temperatures, making them ideal for portable applications and equipment with frequent movement.
Environmental Resistance
Rubber sheathed cables offer excellent resistance to:
- UV radiation and outdoor weathering
- Ozone and atmospheric pollutants
- Temperature extremes from -40°C to +90°C
- Moisture and humidity
- Oil and chemical exposure
Mechanical Durability
The tough rubber construction provides:
- Impact and crush resistance
- Abrasion resistance for dragging applications
- Tear resistance in demanding environments
- Fatigue resistance under repeated flexing
- Vibration resistance in machinery applications
Electrical Performance
Rubber insulation delivers:
- Excellent dielectric properties
- Low power factor for efficient transmission
- Good insulation resistance over time
- Stable electrical characteristics across temperature ranges
- Superior performance in high-frequency applications
Installation Guidelines
Handling and Storage
Proper handling ensures cable longevity:
- Avoid sharp bends below minimum bend radius
- Store in cool, dry conditions away from direct sunlight
- Protect from sharp objects and chemical spills
- Support cable weight to prevent stretching
- Inspect regularly for damage or deterioration
Installation Techniques
Professional installation practices include:
- Use appropriate cable pulling techniques
- Install proper strain relief at terminations
- Maintain minimum bend radius requirements
- Secure cables to prevent movement damage
- Provide adequate support for vertical runs
Connection Methods
Reliable connections require:
- Clean conductor preparation
- Proper terminal selection and crimping
- Appropriate insulation and sealing
- Strain relief at connection points
- Regular inspection and maintenance
Standards and Certifications
International Standards
Rubberised cables must comply with various international standards:
IEC 60245: International standard for rubber insulated cables for rated voltages up to and including 450/750V.
BS 6007: British standard specifying requirements for rubber insulated cables for electric power and lighting.
VDE 0250: German standard for rubber insulated flexible cables and cords.
UL 62: Underwriters Laboratories standard for flexible cords and cables in North America.
Industry Certifications
Quality certifications include:
- CE marking for European compliance
- CSA certification for Canadian markets
- UL listing for North American applications
- KEMA testing for European markets
- CCC certification for Chinese markets
Environmental Compliance
Modern rubber cables meet environmental requirements:
- RoHS compliance for restricted substances
- REACH regulation compliance
- Halogen-free formulations where required
- Recyclability considerations
- Low smoke and fume emissions
Selection Criteria
Electrical Requirements
Proper cable selection considers:
- Voltage rating and insulation class
- Current carrying capacity and conductor size
- Temperature rating for application environment
- Frequency response for AC applications
- Grounding and shielding requirements
Environmental Factors
Application environment assessment includes:
- Operating temperature range
- Chemical exposure potential
- Moisture and water resistance needs
- UV and weather exposure
- Mechanical stress and flexing requirements
Mechanical Properties
Physical performance requirements:
- Flexibility and bend radius
- Tensile strength and elongation
- Abrasion and tear resistance
- Impact and crush resistance
- Fatigue life under repeated flexing
Maintenance and Testing
Routine Inspection
Regular inspection prevents failures:
- Visual examination for cuts, cracks, or damage
- Flexibility testing for insulation degradation
- Connection integrity verification
- Environmental protection assessment
- Documentation of inspection results
Electrical Testing
Periodic electrical testing includes:
- Insulation resistance measurements
- Continuity testing of conductors
- Ground fault testing where applicable
- High-potential testing for critical applications
- Thermal testing under load conditions
Preventive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance extends cable life:
- Cleaning of connections and terminals
- Reapplication of protective coatings
- Replacement of damaged sections
- Upgrading support and protection systems
- Trending of test results over time
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Insulation Degradation
Common causes and solutions:
- Ozone exposure requiring EPDM formulations
- UV degradation needing protective covers
- Chemical attack requiring resistant compounds
- Thermal aging requiring temperature control
- Mechanical damage requiring better protection
Flexibility Loss
Addressing stiffening issues:
- Cold temperature effects on rubber compounds
- Aging and oxidation of rubber materials
- Contamination affecting flexibility
- Improper storage and handling
- Selection of inappropriate rubber type
Connection Problems
Resolving connection failures:
- Corrosion at terminals and connections
- Thermal cycling effects on connections
- Mechanical stress at termination points
- Moisture ingress protection
- Proper strain relief installation
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
Rubber cable costs include:
- Premium materials and manufacturing
- Specialized testing and certification
- Enhanced performance characteristics
- Quality construction and durability
- Compliance with industry standards
Lifecycle Value
Long-term benefits of rubber cables:
- Extended service life in harsh conditions
- Reduced maintenance and replacement costs
- Better performance and reliability
- Lower total cost of ownership
- Reduced downtime and operational disruptions
Application-Specific Economics
Cost analysis varies by application:
- Portable equipment requiring frequent replacement
- Fixed installations with long service life
- Harsh environments with high failure rates
- Critical applications where reliability is paramount
- Safety considerations and insurance implications
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable Manufacturing
Modern rubber cable production emphasizes:
- Reduced environmental impact
- Recyclable rubber compounds where possible
- Energy-efficient manufacturing processes
- Responsible sourcing of raw materials
- Compliance with environmental regulations
End-of-Life Management
Responsible disposal includes:
- Copper recovery from conductors
- Rubber recycling where facilities exist
- Proper disposal of non-recyclable components
- Minimizing landfill waste
- Environmental impact assessment
Future Trends and Innovations
Advanced Rubber Compounds
Ongoing development focuses on:
- Improved temperature resistance
- Enhanced flexibility at low temperatures
- Better chemical and oil resistance
- Reduced environmental impact
- Increased electrical performance
Smart Cable Technology
Integration of monitoring capabilities:
- Temperature sensing within cables
- Insulation condition monitoring
- Mechanical stress detection
- Wireless communication integration
- Predictive maintenance alerts
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental considerations drive:
- Bio-based rubber alternatives
- Improved recyclability
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Sustainable manufacturing practices
- Circular economy integration
Conclusion
Rubberised cables represent an essential solution for applications requiring flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. Their unique combination of electrical performance and mechanical properties makes them indispensable for portable equipment, industrial machinery, and harsh environment installations.
The superior flexibility and environmental resistance of rubber sheathed cables provide significant advantages over rigid alternatives in demanding applications. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure optimal performance and service life, delivering reliable electrical power where conventional cables would fail.
As technology advances and environmental considerations become increasingly important, rubberised cables continue to evolve with improved compounds, sustainable manufacturing practices, and enhanced performance characteristics. For applications requiring the ultimate in flexibility and environmental resistance, rubber insulated cables remain the preferred choice for discerning engineers and electrical professionals worldwide.