Understanding Power and Control Cables in Modern Industry
The distinction between power and control cables represents a fundamental aspect of electrical system design. While power cables deliver electrical energy, types of control cables focus on transmitting signals that manage and monitor industrial equipment operations across manufacturing, energy, and telecommunications sectors.

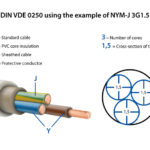
CVVS Control Cable Construction
What Are Control Cables and How Do They Differ from Power Cables?
Power and control cables serve distinctly different purposes in industrial applications. Power cables are designed to carry high-voltage electricity to operate machinery, while control cables transmit low-voltage signals for equipment control, monitoring, and automation systems.
'Understanding the various types of control cables is crucial for proper system design,' explains Dr. Sarah Mitchell, electrical engineering professor at Industrial Technology Institute. 'Each type serves specific applications, and selecting the wrong cable type can compromise entire control systems.'
Comprehensive Guide to Types of Control Cables
Multi-Core Control Cables
Multi-core control cables represent the most versatile category among types of control cables. These cables feature multiple insulated conductors within a single protective jacket, typically ranging from 2 to 61 cores. Multi-core designs optimize space utilization while providing multiple signal paths for complex industrial control applications.
Armored control cables
provide superior mechanical protection for demanding industrial environments. These specialized types of control cables incorporate steel wire armor or metallic tape shielding, making them ideal for underground installations, chemical plants, and heavy industrial facilities where physical protection is paramount.
Flexible Control Cables
Among types of control cables, flexible variants cater specifically to applications requiring continuous movement. Flexible control cables feature enhanced conductor flexibility and specialized insulation materials that prevent fatigue during repetitive motion in robotic systems, crane applications, and mobile machinery.
Shielded Control Cables
Shielded control cables address electromagnetic interference challenges in sensitive industrial environments. These types of control cables incorporate various shielding techniques including foil shields, braided shields, or combination shielding to ensure signal integrity in electrically noisy environments.
Fire-Resistant Control Cables
Safety-critical applications demand fire-resistant control cables that maintain functionality during emergency conditions. These specialized types of control cables feature flame-retardant materials and enhanced insulation systems that continue operating even under fire conditions.
Power and Control Cables: Key Differences and Applications
Voltage and Current Specifications
Power and control cables operate at vastly different electrical parameters. Power cables typically handle voltages from 600V to several kilovolts with high current capacity, while control cables operate at low voltages (typically under 600V) with minimal current requirements.
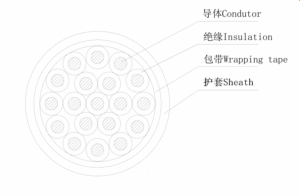
CVV Control Cable Construction
Construction Differences
The construction of power and control cables reflects their distinct functions. Power cables emphasize conductor size and insulation thickness for electrical capacity, while types of control cables prioritize signal integrity, shielding effectiveness, and multi-conductor configurations.
Installation Requirements
Power and control cables require different installation approaches. Power cables need substantial support structures and separation distances, while types of control cables focus on electromagnetic compatibility and proper grounding techniques.
Industrial Applications of Different Types of Control Cables
Manufacturing Automation
Types of control cables play critical roles in programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS), and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). Power and control cables work together to create comprehensive automation solutions, with power cables energizing equipment and control cables managing operations.
Energy Sector Implementation
Power generation facilities utilize various types of control cables for monitoring turbines, generators, and grid management systems. The integration of power and control cables enables sophisticated energy management and protection systems across renewable and conventional power plants.
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Modern telecommunications rely on specialized types of control cables for network equipment management, base station control, and data center operations. These applications demand high-frequency signal transmission capabilities distinct from traditional power and control cables.
Technical Specifications for Types of Control Cables
Conductor Materials and Configurations
Types of control cables typically utilize copper conductors for optimal conductivity and signal integrity. Conductor configurations vary from solid wire for permanent installations to stranded conductors for flexible applications requiring frequent movement.
Insulation Systems
Different types of control cables employ various insulation materials including:
- PVC Control Cables: Cost-effective solutions for standard industrial applications
- XLPE Control Cables: Enhanced temperature and chemical resistance
- Silicone Control Cables: High-temperature applications up to 180°C
- Fluoropolymer Control Cables: Chemical resistance and extreme temperature performance
Shielding Technologies
Types of control cables incorporate diverse shielding approaches:
- Foil Shielded Cables: Lightweight electromagnetic interference protection
- Braided Shield Cables: Superior mechanical durability and grounding effectiveness
- Combination Shielded Cables: Maximum protection for critical applications
Market Trends in Power and Control Cables
The global market for power and control cables continues expanding, driven by industrial automation and smart manufacturing initiatives. Industry analysts report increasing demand for specialized types of control cables including:
- Ethernet Control Cables for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applications
- Bus Cables for fieldbus communication systems
- Servo Motor Cables for precision motion control applications
Market projections indicate the power and control cables sector will reach $18.5 billion by 2028, reflecting the critical role these components play in modern industrial infrastructure.
Selection Criteria for Types of Control Cables
Environmental Considerations
Selecting appropriate types of control cables requires careful evaluation of environmental conditions including temperature extremes, chemical exposure, moisture levels, and mechanical stress factors.
Signal Requirements
Different types of control cables suit various signal transmission needs:
- Analog Signal Cables: Continuous signal transmission with minimal interference
- Digital Signal Cables: Binary data transmission with high noise immunity
- Mixed Signal Cables: Combined analog and digital transmission capabilities
Regulatory Compliance
Types of control cables must comply with relevant international standards including IEC 60227, BS 5308, and UL standards for North American applications. Compliance ensures consistent performance and safety across global installations.
Installation Best Practices for Power and Control Cables
Separation Requirements
Proper installation of power and control cables demands adequate separation to prevent electromagnetic interference. Control cables should maintain minimum distances from power cables based on voltage levels and power ratings.
Cable Management Systems
Effective power and control cables installations utilize structured cable management including cable trays, conduits, and separation barriers that organize different types of control cables while facilitating maintenance access.
Grounding and Shielding
Proper grounding techniques for types of control cables ensure effective electromagnetic interference mitigation and personnel safety. Shield grounding methods vary based on system architecture and signal frequencies.
Future Developments in Types of Control Cables
Smart Cable Technologies
Emerging types of control cables incorporate embedded sensors and communication capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring of cable condition, temperature, and electrical parameters.
Enhanced Materials
Advanced materials development continues improving types of control cables performance through:
- Nanotechnology-Enhanced Insulation: Superior electrical and thermal properties
- Bio-Based Materials: Environmentally sustainable cable compounds
- Self-Healing Polymers: Extended service life through automatic damage repair
Industry 4.0 Integration
Power and control cables evolution supports Industry 4.0 initiatives through enhanced data transmission capabilities, predictive maintenance features, and integration with digital twin technologies.
Conclusion: Optimizing Power and Control Cables Selection
Understanding the various types of control cables and their relationship to power and control cables systems is essential for successful industrial electrical design. Proper selection of control cable types ensures reliable signal transmission, electromagnetic compatibility, and long-term system performance.
As industrial automation and digitalization continue advancing, the importance of selecting appropriate types of control cables will only increase. Engineers and system designers must consider application requirements, environmental conditions, and future expansion needs when specifying power and control cables for industrial installations.
The synergy between power and control cables creates the foundation for modern automated systems, enabling precise control and monitoring capabilities that drive industrial efficiency and innovation across all sectors.