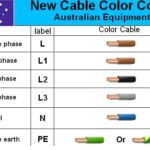
When dealing with outdoor electrical installations, marine applications, or wet environments, regular electrical wire simply won't suffice. Waterproof wire provides the protection and reliability needed for these challenging conditions. Understanding the different types, applications, and installation methods will help you choose the right waterproof wire for your specific project.
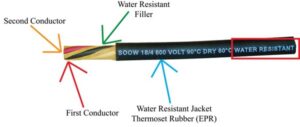
water proof wire
What Is Waterproof Wire?
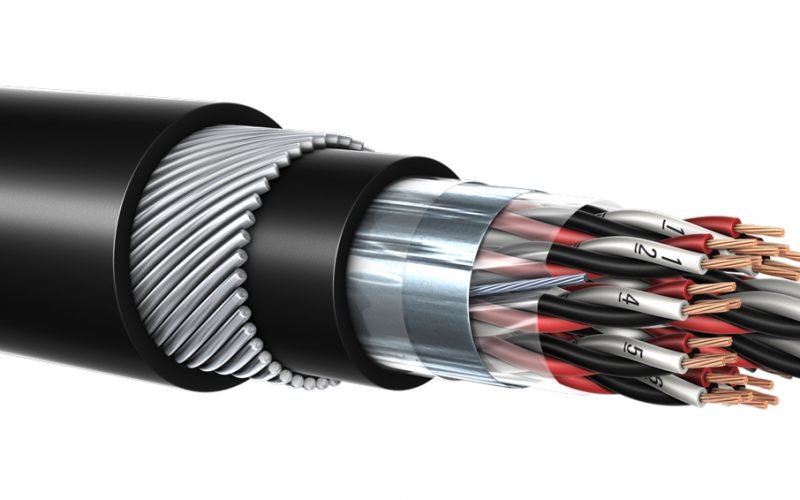
Waterproof wire, also known as water-resistant or marine-grade wire, is specially designed electrical cable that can withstand exposure to moisture, water, and harsh environmental conditions. Unlike standard electrical wire, waterproof wire features enhanced insulation, specialized jacketing, and sometimes sealed construction to prevent water ingress.
Key Characteristics:
- Water-resistant outer jacket
- Enhanced insulation materials
- Corrosion-resistant conductors
- UV-resistant properties
- Temperature tolerance
- Chemical resistance
Types of Waterproof Wire
1. Marine Wire
Primary Features:
- Tinned copper conductors prevent corrosion
- XLPE or silicone insulation
- Flame-retardant properties
- Salt water resistance
- Temperature range: -40°F to 221°F
Common Applications:
- Boat electrical systems
- Marine lighting
- Navigation equipment
- Bilge pumps
- Shore power connections
2. Burial-Rated Cable
Design Specifications:
- Heavy-duty polyethylene jacket
- Direct burial capability
- Moisture barrier protection
- Rodent-resistant construction
- Long-term underground stability
Typical Uses:
- Underground electrical runs
- Landscape lighting systems
- Outdoor power distribution
- Irrigation control systems
- Security camera installations
3. Submersible Wire
Special Properties:
- Completely waterproof construction
- Pressure-resistant design
- Flexible even when wet
- Low-voltage applications
- Sealed connector compatibility
Applications:
- Submersible pumps
- Pond and fountain equipment
- Underwater lighting
- Well pump connections
- Aquarium systems
4. Outdoor Extension Cords
Weather-Resistant Features:
- Heavy-duty rubber or vinyl jacket
- Reinforced plug connections
- UV stabilized materials
- Cold weather flexibility
- SJTW or SJEOW ratings
Common Uses:
- Outdoor power tools
- Holiday lighting
- Temporary power needs
- Construction sites
- Event installations
Wire Ratings and Standards
IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
Understanding IP ratings helps select appropriate waterproof wire:
IP65: Dust-tight and protected against water jets IP66: Dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets IP67: Dust-tight and protected against temporary immersion IP68: Dust-tight and protected against continuous submersion
NEMA Ratings
NEMA 4X: Weather-resistant and corrosion-resistant NEMA 6P: Submersible and pressure-resistant NEMA 7: Explosion-proof for hazardous locations
UL and AWG Standards
UL Listed: Safety certification for electrical products AWG Ratings: Wire gauge specifications for current capacity Temperature Ratings: Operating temperature ranges Voltage Ratings: Maximum voltage handling capacity
Applications and Use Cases
Residential Applications
Outdoor Lighting Systems:
- Landscape lighting installations
- Security flood lights
- Pathway and garden lighting
- Holiday decoration connections
- Pool and spa lighting
Home Automation:
- Outdoor security cameras
- Irrigation system controls
- Gate and garage door operators
- Outdoor speakers and entertainment
- Smart home sensors
Commercial Applications
Building Exteriors:
- Sign lighting and displays
- Parking lot lighting
- Building security systems
- HVAC outdoor units
- Emergency lighting systems
Industrial Uses:
- Manufacturing equipment
- Warehouse applications
- Agricultural systems
- Mining operations
- Chemical processing facilities
Marine and Aquatic Applications
Boat Electrical Systems:
- Engine compartment wiring
- Navigation light circuits
- Bilge pump connections
- Radio and GPS installations
- Charging system wiring
Dock and Marina:
- Shore power pedestals
- Dock lighting systems
- Boat lift controls
- Security systems
- Utility connections
Agricultural Applications
Farm Operations:
- Irrigation control systems
- Barn and shed wiring
- Equipment power supplies
- Livestock water systems
- Grain handling equipment
Selecting the Right Waterproof Wire
Environmental Considerations
Temperature Extremes:
- Arctic conditions: Silicone insulated wire
- High heat: THHN or XLPE insulation
- Variable temperatures: Multi-rated cables
- Thermal cycling: Flexible constructions
Chemical Exposure:
- Oil resistance: Neoprene jacketed wire
- Acid environments: Teflon insulated cables
- Salt water: Tinned copper conductors
- Cleaning chemicals: Chemical-resistant jackets
Physical Stress:
- Frequent flexing: Extra-flexible constructions
- Mechanical protection: Armored cables
- Rodent damage: Steel-tape armor
- Abrasion resistance: Tough outer jackets
Electrical Requirements
Current Capacity:
- Calculate load requirements
- Consider voltage drop over distance
- Account for ambient temperature
- Include safety margins
Voltage Requirements:
- Low voltage: 12V-24V systems
- Line voltage: 120V-240V applications
- High voltage: Industrial applications
- DC vs AC considerations
Installation Best Practices
Proper Planning
Route Selection:
- Avoid sharp bends and corners
- Plan for thermal expansion
- Consider accessibility for maintenance
- Minimize exposure to damage
Connection Points:
- Use waterproof connectors
- Apply dielectric grease
- Ensure proper sealing
- Plan for disconnection needs
Installation Techniques
Underground Installation:
- Proper burial depth (typically 18-24 inches)
- Use warning tape above cables
- Backfill with suitable materials
- Mark cable locations
Above-Ground Installation:
- Secure cables properly
- Provide drip loops
- Use appropriate supports
- Protect from physical damage
Connection Methods
Waterproof Connectors:
- Heat-shrink connectors with sealant
- Twist-on wire nuts with silicone
- Compression connectors
- Sealed junction boxes
Sealing Techniques:
- Electrical tape with self-amalgamating tape
- Heat-shrink tubing with adhesive
- Liquid electrical tape
- Silicone sealants
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Installation Errors
Inadequate Protection:
- Using indoor-rated wire outdoors
- Insufficient burial depth
- Poor connection sealing
- Ignoring UV exposure
Improper Sizing:
- Undersized conductors
- Inadequate ampacity calculations
- Ignoring voltage drop
- Wrong insulation rating
Maintenance Oversights
Regular Inspection:
- Check for jacket damage
- Verify connection integrity
- Monitor for corrosion
- Test insulation resistance
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
Wire Costs:
- Marine wire: $1-5 per foot
- Burial cable: $0.50-3 per foot
- Submersible wire: $2-8 per foot
- Specialty cables: $5-20 per foot
Installation Costs:
- Professional installation: $3-10 per foot
- Trenching and burial: $2-5 per foot
- Connector and junction costs
- Testing and certification
Long-Term Value
Reliability Benefits:
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Fewer service calls
- Extended service life
- Improved safety
Performance Advantages:
- Consistent electrical performance
- Weather independence
- Corrosion resistance
- Reduced downtime
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Water Ingress Problems
Symptoms:
- Intermittent electrical faults
- Ground fault circuit breaker trips
- Corrosion at connections
- Reduced insulation resistance
Solutions:
- Improve sealing methods
- Replace damaged sections
- Upgrade connection types
- Install drainage systems
Mechanical Damage
Prevention:
- Proper cable protection
- Adequate support systems
- Correct installation depth
- Regular inspection schedules
Future Trends and Innovations
Advanced Materials
New Insulation Technologies:
- Cross-linked polyethylene improvements
- Silicone compound advances
- Fluoropolymer developments
- Composite jacket materials
Smart Wire Technologies:
- Integrated monitoring systems
- Self-healing materials
- Temperature-sensing capabilities
- Fault location systems
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable Options:
- Recyclable jacket materials
- Lead-free constructions
- Environmentally friendly manufacturing
- Energy-efficient production methods
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Monthly Checks:
- Visual inspection for damage
- Connection tightness verification
- Moisture detection
- Performance testing
Annual Inspections:
- Comprehensive system testing
- Insulation resistance measurement
- Thermal imaging analysis
- Documentation updates
Testing Methods
Insulation Testing:
- Megohm meter testing
- Hipot testing procedures
- Ground fault detection
- Continuity verification
Conclusion
Waterproof wire is essential for reliable electrical installations in wet, outdoor, and marine environments. Selecting the appropriate type based on environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and application needs ensures long-term performance and safety.
Whether you're installing landscape lighting, marine electrical systems, or industrial equipment, understanding the various types of waterproof wire and their applications helps you make informed decisions. Proper installation techniques, quality connections, and regular maintenance are crucial for maximizing the benefits of waterproof wire systems.
Investing in quality waterproof wire may cost more initially, but the long-term reliability, safety, and reduced maintenance make it a cost-effective choice for any application exposed to moisture or harsh environmental conditions. Always consult with electrical professionals for complex installations and ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.
Remember that while waterproof wire provides excellent protection against moisture, proper installation and sealing of connections are equally important for system reliability and safety.