Understanding Cable Powers: What You Need to Know About Power Transmission in Cables
When we talk about cable powers, we're often referring to the ability of cables to handle and transmit electrical power. This includes their capacity to carry different levels of electric current, voltage, and signal strength, depending on the type of cable and its application. In this article, we’ll dive into the concept of cable powers, explore what it means for cables to have specific powers, and discuss how to choose the right cables for various applications.

what are cables powers
What is Meant by 'Cable Powers'?
The term 'cable powers' generally refers to the electrical power transmission capacity of a cable, meaning how much electricity the cable can carry safely. This power capability depends on several factors, such as:
Voltage Rating: The maximum electrical potential a cable can handle without the insulation breaking down.
Current Rating: The maximum electrical current (measured in amperes) that can pass through the cable without causing overheating or damage.
Power Handling: The amount of electric power (measured in watts or kilowatts) that the cable can transmit.
Understanding a cable's power capabilities is essential when selecting cables for specific applications, whether it’s for residential wiring, industrial machinery, or telecommunication systems.
How Do Cables Handle Power?
Cables are designed to carry electricity or signals from one point to another. The power capabilities of a cable depend on:
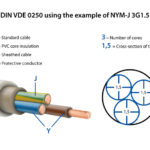
Conductor Size: The thicker the conductor, the more power it can handle. Power cables are made with copper or aluminum conductors that carry the electric current. Larger cables, such as 12 AWG (American Wire Gauge) or 6 AWG, can carry more power than smaller cables like 18 AWG.
Insulation Material: Insulation around the conductor prevents power from leaking out of the cable. Materials like PVC, XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene), or rubber are used to insulate the wires. The better the insulation, the more power the cable can carry without overheating or causing a short circuit.
Cable Type and Construction: Different types of cables are built for different power handling capacities. For example, high-voltage power cables are designed to handle tens of thousands of volts, whereas low-voltage cables are meant for everyday applications, such as home appliances.
How Much Power Can a Cable Carry?
The amount of power a cable can carry is typically determined by two key factors:
Voltage Rating: This tells you the maximum electrical potential the cable can handle. Power cables have voltage ratings such as 300V, 600V, or 1000V for common applications. Higher-voltage cables are used for industrial and high-power applications.
Current Rating: The current rating is the maximum amount of current a cable can safely carry. This is usually measured in amps. The current rating is crucial because too much current can cause a cable to overheat, potentially causing a fire or failure of the insulation.
Example of Power Handling:
A 12 AWG copper wire with PVC insulation can typically handle up to 20-25 amps. The total power capacity (in watts) is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current. For example, at 120V, a 12 AWG wire can handle up to about 2,400 watts (120V * 20A = 2,400W).
For heavier-duty applications, cables like 6 AWG can handle much higher power, such as 55-60 amps, making them suitable for industrial machinery or power distribution systems.
Types of Cables Based on Power Transmission
Low Voltage Power Cables:
Voltage Rating: Below 1,000V.
Applications: Commonly used in residential and light commercial settings, such as for powering appliances, lighting systems, and small electrical devices.
Power Handling: These cables are designed to carry moderate levels of power, often up to 20-30 amps.
Medium Voltage Power Cables:
Voltage Rating: Between 1,000V and 35,000V.
Applications: Used for powering large industrial equipment, substations, and municipal power distribution systems.
Power Handling: These cables carry more power, up to 50-100 amps or higher, depending on the size and construction.
High Voltage Power Cables:
Voltage Rating: Above 35,000V.
Applications: Used for long-distance power transmission, typically in national grids and large-scale power plants.
Power Handling: These cables are capable of transmitting gigawatts of power over long distances and require robust insulation to ensure safety.
Factors Affecting Cable Power Handling
Temperature: Cables have specific temperature ratings (e.g., 60°C, 75°C, or 90°C) that define how much current they can carry without overheating. High temperatures can cause cables to degrade and affect their ability to carry power safely.
Environmental Conditions: The external environment where the cable is used also impacts its power capacity. For instance, underground cables need additional insulation and protection, while aerial cables need to withstand UV exposure and harsh weather conditions.
Cable Length: The longer the cable, the greater the potential for power loss due to resistance. For very long distances, special cables with additional insulation and materials may be needed to maintain power integrity.
Voltage Drop: Over long distances, there’s a phenomenon called voltage drop, where the voltage decreases due to the resistance in the cable. This can reduce the amount of power that reaches the end device, especially if the cable is too thin for the amount of current being carried.
Importance of Choosing the Right Power Cable
Choosing the right cable with the appropriate power handling capacity is essential for both safety and efficiency. If a cable is too small for the current or voltage it needs to carry, it can lead to overheating, fires, or even equipment failure.
Here’s how to ensure you choose the right cable:
Check the Voltage: Ensure the cable’s voltage rating matches or exceeds the voltage of your electrical system.
Assess Current Needs: Match the cable’s ampacity (current-carrying capacity) with the amount of power your system requires.
Consider Environmental Factors: For outdoor applications, ensure you choose a cable that is rated for UV protection, moisture resistance, and mechanical protection.
Applications of Power Cables in Different Industries
Residential: Power cables in homes connect appliances, lighting, and heating systems. The power requirements typically range from 10 amps to 30 amps for standard household wiring.
Commercial and Industrial: These environments require higher-power cables to handle larger loads, such as air conditioning systems, heavy machinery, and lighting systems. Cables rated for medium voltage (up to 35,000V) are often used here.
Energy and Utility: In the power industry, high-voltage cables are essential for long-distance transmission of electricity through national grids and undersea cables.
Automotive: Power cables in vehicles and electric cars transmit energy to motors, battery systems, and lighting, and are designed to handle specific power loads for the vehicle's operation.
Renewable Energy: Solar power systems, wind farms, and other renewable energy installations rely on power cables to carry the electricity generated by solar panels or wind turbines to the grid.
Conclusion
In summary, cable powers refer to the capacity of a cable to carry electricity, determined by factors like voltage rating, current carrying capacity, and the cable’s design and construction. Understanding these power characteristics is essential for choosing the right cable for your needs, whether for low-voltage residential use or high-voltage industrial applications. Always ensure that the cable is suited to the power demands of your specific application to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability.