What Does Fiber Optic Cable Look Like?
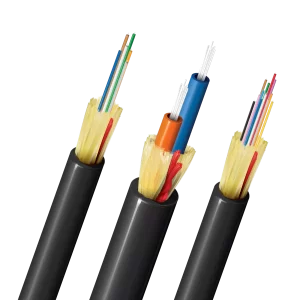
what does fiber optic cable look like
Fiber optic cables have a distinctive appearance compared to traditional copper cables. These cables are known for their thin, flexible structure, designed to handle high-speed data transmission over long distances. In this article, we’ll break down the physical features of fiber optic cables to help you understand what they look like.
1. Outer Jacket
The outer jacket of a fiber optic cable is typically made of plastic or PVC, which protects the internal fibers from external damage.
Color: The jacket color can vary depending on the type of fiber inside. For instance, yellow jackets are common for single-mode fiber cables, while orange or aqua jackets are used for multi-mode fiber cables.
Texture: The outer layer is usually smooth, but depending on whether the cable is meant for indoor or outdoor use, it can also be more rugged to withstand environmental conditions.
2. Fiber Core
The core of a fiber optic cable is the central, transparent section where the data (in the form of light signals) travels. The core is made of either glass or plastic.
Size: The core is incredibly small, typically around 8 to 10 microns in diameter for single-mode fiber and 50 to 100 microns for multi-mode fiber.
Appearance: The core is almost invisible to the naked eye, but under magnification, it looks like a tiny, clear strand of glass or plastic.
3. Cladding
Surrounding the core is the cladding, which is also made of glass or plastic but has a different refractive index than the core.
Purpose: The cladding reflects light back into the core, ensuring that light signals stay within the fiber as they travel along the cable.
Appearance: The cladding is typically clear or slightly tinted. It’s usually only visible when the cable is cut open or stripped.
4. Buffer Coating
The buffer coating is a protective plastic layer that surrounds the cladding, providing an extra layer of protection to the fragile fibers inside the cable.
Appearance: The buffer is usually clear or light-colored, making it easy to distinguish from the outer jacket of the cable.
5. Strength Members
Many fiber optic cables, especially those used outdoors, have strength members inside to prevent the cable from breaking under tension.
Material: These strength members are often made from materials like Kevlar or steel and are visible when the outer jacket is stripped.
Appearance: The strength members are often thin, white or silver fibers that run along the length of the cable. They help reinforce the cable without compromising flexibility.
6. Cross-Section of Fiber Optic Cable
If you were to cut open a fiber optic cable, you would see a few clear layers:
Outer Jacket: The protective layer that is typically colored black, yellow, or orange.
Strength Members: These are visible as thin strands inside the cable, providing structural support.
Buffer Coating: A clear layer that surrounds the cladding.
Cladding: The transparent layer around the core.
Core: The innermost part of the cable, where light travels, which is a very thin strand of glass or plastic.
7. Different Types of Fiber Optic Cables
Single-Mode Fiber: These cables are typically used for long-distance data transmission. They have a small core (around 8-10 microns) and are generally identified by a yellow jacket.
Multi-Mode Fiber: These cables are used for shorter distances and have a larger core (50 to 100 microns). They are often recognized by an orange or aqua jacket.
8. Indoor vs. Outdoor Fiber Optic Cables
Indoor Cables: These cables are designed to be flexible and lightweight with a thinner outer jacket. They are more common in office environments and homes.
Outdoor Cables: These have a heavier, more durable jacket, often made of weather-resistant material to protect the cable from UV rays, moisture, and physical damage. They may also feature an armored layer for added protection.
Conclusion
Fiber optic cables are easily recognizable by their thin, flexible design and layered construction. The outer jacket color helps identify the type of fiber, while the core and cladding are crucial for transmitting light signals. Whether it’s for single-mode or multi-mode fiber, understanding the components of fiber optic cables helps in recognizing their functionality and application in today’s high-speed data networks.