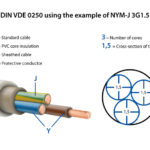
A cable is a bundle of one or more wires or fibers that are enclosed in a protective covering and used to transmit electrical power, data, or signals between devices or systems. Cables come in various shapes, sizes, and materials depending on their intended use, and they are essential in a wide range of applications—from networking and telecommunications to electrical wiring and even in transportation (like cables used in elevators or cranes).

What is cable
Types of Cables:
Electrical Cables
These cables are used to carry electrical power from one point to another. They can be found in homes, industrial settings, and infrastructure. Electrical cables can be further categorized based on their voltage rating and insulation material, such as:Power Cables: Designed for carrying high voltage electrical current.
AC (Alternating Current) Cables: Specifically used for alternating current applications, typically found in households and businesses.
DC (Direct Current) Cables: Used for direct current power transmission, often in specialized applications like battery-powered systems.
Coaxial Cables
These are used for transmitting radio frequency (RF) signals. Common in television and internet connections, coaxial cables are designed with an inner conductor, insulating layer, shielding, and outer layer to protect the signal from external interference.Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables use strands of glass or plastic to transmit light signals, which can carry a lot of data over long distances with minimal signal loss. These are widely used in high-speed internet and telecommunications networks.Data Cables
Data cables are used to transfer digital information between devices. Examples include:USB Cables: Commonly used for connecting devices like smartphones, computers, and printers.
Ethernet Cables: Used for networking to connect devices like computers, routers, and switches in local area networks (LANs).
HDMI Cables: High-definition multimedia interface cables used to transfer high-definition video and audio signals.
Audio/Video Cables
These are used to transmit sound or video signals between devices. Common examples include:RCA Cables: Used to transmit audio and video signals to TVs, DVD players, etc.
3.5mm Stereo Cables: Often used to connect audio devices such as headphones or speakers to a sound source like a phone or computer.
Components of a Cable:
Conductors: The wires inside the cable that carry electrical current or signals. These are usually made of copper or aluminum.
Insulation: A non-conductive material that surrounds the conductor(s) to prevent short circuits and protect against electrical shocks.
Shielding: A layer of material, often made of copper or aluminum, that protects the signals from interference or external noise, ensuring a clean transmission.
Jacket: The outer protective layer that guards the internal components of the cable from environmental damage, like physical wear, moisture, and UV rays.
Uses of Cables:
Power Distribution: To transport electrical energy from power sources to electrical appliances, machines, and infrastructure.
Telecommunications: For transmitting telephone, internet, and television signals.
Networking: To connect devices in local area networks (LANs) or wide area networks (WANs), allowing data sharing between computers, printers, servers, and other devices.
Audio/Visual Connections: Used in home theaters, audio equipment, and computer peripherals to transmit sound and video signals.
Industrial Applications: Cables are widely used in factories, plants, and machines to power equipment or control systems.
Conclusion:
Cables are essential components that enable modern electrical systems, data networks, and entertainment devices to function. By understanding the different types and uses of cables, you can make informed choices when selecting cables for various applications. Whether it’s powering your home appliances, connecting to the internet, or transmitting high-definition video, cables are crucial for maintaining a seamless flow of energy and information.