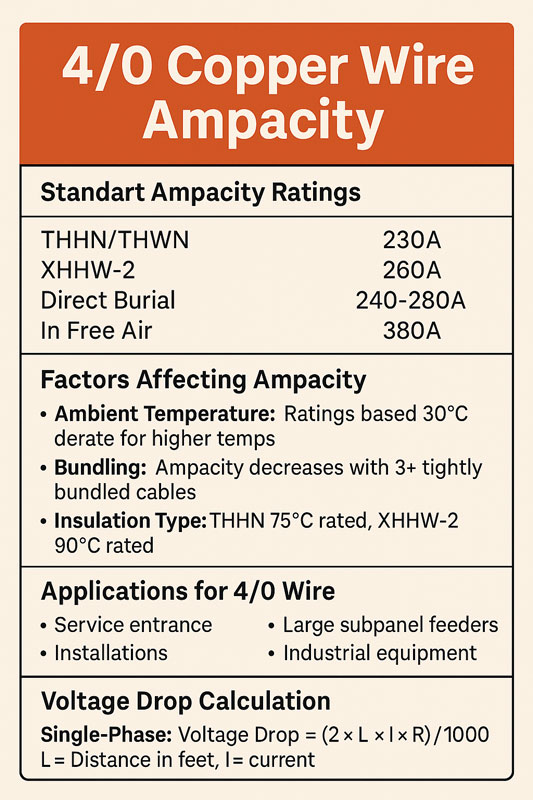
The ampacity of 4/0 copper wire typically ranges from 230 to 380 amps, depending on the insulation type and installation method. For example, with THWN insulation, it handles 230 amps, while XHHW-2 insulation supports up to 260 amps. In free air, bare 4/0 copper wire can carry as much as 380 amps. Keep reading for a full breakdown based on NEC standards, temperature ratings, voltage drop, and real-world applications.
4 0 copper wire ampacity
What is 4/0 Copper Wire Ampacity?
4/0 copper wire ampacity refers to the maximum electrical current that a 4/0 AWG (American Wire Gauge) copper wire can carry under specific conditions without overheating. Also known as “0000” or “four-aught,” this conductor size is one of the largest in the AWG system. Understanding ampacity is crucial for electricians, engineers, and contractors handling high-current electrical systems.
Standard 4/0 Copper Wire Ampacity Ratings
Ampacity varies by installation type, insulation material, and ambient temperature. Below are typical NEC-based ampacity values:
Key Ampacity Ratings (Based on Insulation Type)
-
THWN/THHN (75°C): 230 amps
-
XHHW/XHHW-2 (90°C): 260 amps
-
Bare copper in free air: 380 amps
-
Direct burial: 240–280 amps (depends on soil thermal resistance)
Installation Methods and Their Impact
-
Conduit installation: 230A (typical for THWN)
-
Cable tray with spacing: 250–270A
-
Direct burial: 240–280A
-
Free air: Up to 380A with proper ventilation
Factors Affecting 4/0 Copper Wire Ampacity
Ambient Temperature Derating
Ampacity ratings assume 30°C (86°F) ambient. Higher temperatures reduce capacity:
-
40°C → 0.88 × rated ampacity
-
50°C → 0.75 × rated ampacity
-
60°C → 0.58 × rated ampacity
Bundled Conductor Adjustment
When multiple conductors are run together:
-
4–6 wires: Use 80% of rated ampacity
-
7–9 wires: Use 70%
-
10 or more: Use 50%
Insulation Type
-
THWN-2: 75°C, 230A
-
XHHW-2: 90°C, 260A
-
RHH/RHW-2 & USE-2: 90°C, 260A
Common Applications of 4/0 Copper Wire
Residential Use
-
Main service entrances
-
Large subpanel feeders
-
EV chargers (Level 2 and above)
-
Pool and spa systems
Commercial & Industrial Use
-
HVAC motor feeders
-
Main panel feeders
-
Welding equipment
-
Data center UPS and power circuits
Renewable Energy & Backup Systems
-
Solar inverter wiring
-
Battery banks
-
Generator transfer switches
Voltage Drop Calculations for 4/0 Copper Wire
Minimizing voltage drop ensures efficiency. Use these formulas:
Single-Phase
Voltage Drop = (2 × L × I × R) ÷ 1000
Three-Phase
Voltage Drop = (1.732 × L × I × R) ÷ 1000
Where:
-
L = wire length (ft)
-
I = current (amps)
-
R = resistance (0.049 ohms/1000 ft for 4/0 copper)
NEC Voltage Drop Limits
-
Branch circuit: ≤3%
-
Feeder: ≤3%
-
Total (branch + feeder): ≤5%
Installation Guidelines
Conduit Sizing (Typical)
-
1× 4/0 wire: 1¼″ conduit
-
3× 4/0 wires: 2″ conduit
-
4× 4/0 wires: 2½″ conduit
Minimum Bending Radius
-
NEC recommends ≥8× conductor diameter
-
For 4/0 copper: ~3' minimum radius
Terminal Connections
-
Use lugs rated for 4/0 size
-
Follow torque specs
-
Clean and prep conductor ends properly
-
Use antioxidant compound if applicable
Copper vs. Aluminum for 4/0 Conductors
| Feature | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | More expensive | Lower upfront cost |
| Durability | More corrosion-resistant | Needs antioxidant paste |
| Size for Same Amp | Smaller diameter | Larger size needed |
Though copper is more costly, it provides better long-term performance and reliability.
Code Compliance and Safety
NEC Compliance
-
Ensure proper ampacity calculations
-
Follow derating requirements
-
Use correct overcurrent protection
-
Adhere to bonding and grounding standards
Safety Tips
-
Do not exceed ampacity limits
-
Maintain proper spacing and ventilation
-
Use PPE during installation and inspection
-
Follow all local codes and permit processes
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
What to Inspect
-
Terminal torque and tightness
-
Insulation wear or burn marks
-
Moisture ingress or chemical exposure
-
Signs of overheating or arc faults
Common Issues
-
Loose lugs → overheating
-
Overloaded conductors → insulation breakdown
-
Poor routing or bending → mechanical damage
Conclusion: Why 4/0 Copper Wire Ampacity Matters
Understanding the ampacity of 4/0 copper wire is essential for safe and efficient power distribution. With standard ampacities ranging from 230A to 380A depending on conditions, this conductor is well-suited for demanding residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Proper selection, derating, installation, and regular inspection help ensure code compliance, minimize energy losses, and extend the life of the electrical system.
Where to Buy 4/0 Copper Wire
Looking for high-quality 4/0 copper wire at competitive prices? Visit TOT Wire & Cable — your trusted supplier for industrial-grade electrical cables. We offer a wide range of copper wire types, including THHN, XHHW-2, and direct burial options, with fast shipping and expert support. Whether you're working on residential, commercial, or industrial projects, you'll find the right cable for your application.
👉 Shop now at TOTCables.com and get the best value on reliable, code-compliant copper wire!