A conductor with single-layer or multi-layer aluminum strands twisted together and an insulating layer extruded on the outside
The term 'overhead line' is in contrast to 'cable'. It refers to a power transmission line where conductors are supported at a certain height by poles or towers to transmit electrical energy. For high-voltage transmission and distribution networks, the insulation of overhead lines from the ground is generally achieved through air. Previously, distribution lines (below 10 kV except for 380 V) typically used bare conductors. However, due to the complex distribution environment in urban areas, short circuits, ground faults, and lightning strikes to lines frequently occur, resulting in reduced power supply reliability. Therefore, nowadays, overhead lines below 10 kV generally adopt insulated conductors (i.e., conductors with an outer insulating layer), which are known as insulated overhead lines.
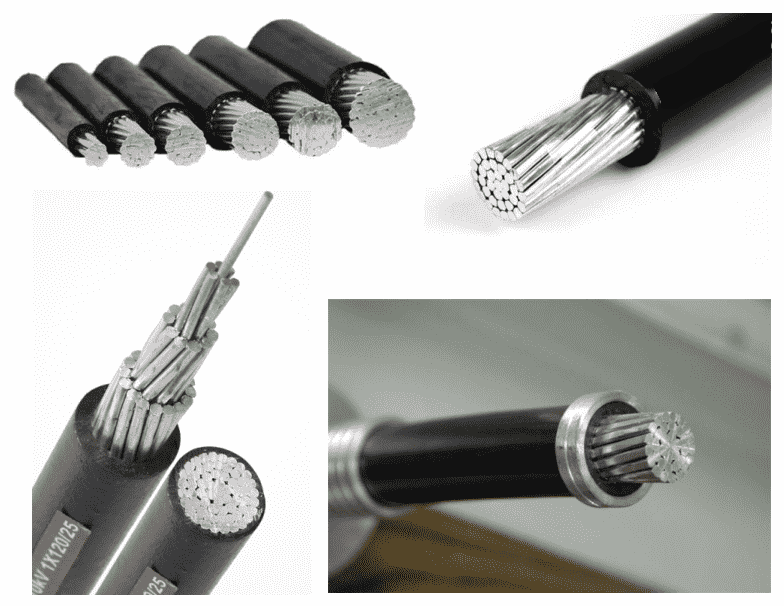
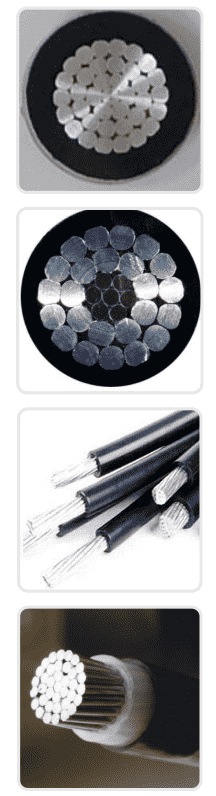
Aerial insulation line can be classified as low-voltage (1 kV) and high-voltage (10 kV), and they also differ in whether they have a steel core or not.
Common models:
JKLYJ: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated overhead cable
JKTRYJ: Flexible copper-core XLPE insulated overhead cable
JKLYJ/Q: Lightweight XLPE insulated overhead cable
JKLGYJ, JKLGYJ/Q: Steel-cored aluminum strand XLPE insulated overhead cable
JKYJ: Copper-core XLPE insulated overhead cable






