Fluoroplastic Cable, specifically refers to wires and cables with fluoroplastic as the outer sheath. Fluoroplastic cables have excellent weather resistance, heat resistance, low friction coefficient, stable chemical properties, and good electrical insulation performance. Therefore, fluoroplastic cables play important roles in harsh environments such as petroleum, metallurgy, chemical, electric power, and aerospace industries. In wire and cable production, commonly used fluoroplastics include polytetrafluoroethylene, perfluoroethylene propylene, polyvinylidene fluoride, tetrafluoroethylene and ethylene copolymer, etc., which are used to manufacture various heat-resistant and high-temperature insulated wires, well logging cables, geological exploration cables, heating cables, class F and H motor lead wires, radiation-resistant wires, electromagnetic wires, RF coaxial cables, and type A flame-retardant cables for coal mines.
Types: Fluoroplastic cables can be manufactured in solid core and insulated forms. Physical foam fluoroplastic cables are already produced and used abroad, while they are still under development in China. When we normally talk about fluoroplastic cables, we usually refer to solid core fluoroplastic cables.
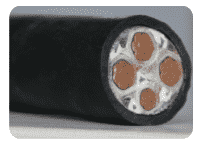
Common Models:
FF Copper core fluoroplastic insulated fluoroplastic sheathed power cable
ZR-FF Copper core fluoroplastic insulated flame-retardant 105°C PVC sheathed power cable
KFF Copper core fluoroplastic insulated fluoroplastic sheathed control cable
KFFP Copper core fluoroplastic insulated fluoroplastic sheathed copper wire braided shielded control cable
KFVP Copper core fluoroplastic insulated flame-retardant 105°C PVC sheathed copper wire braided shielded control cable
Production Range: Common structures: 3+1, 4+1, 3+2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 cores, 4-37 cores for control cables Cross-sections (mm²): 1, 1.5, 2.5, 4, 6, 10, 16, 25, 35, 50, 70, 95, 120, 150, 185, 240, 300
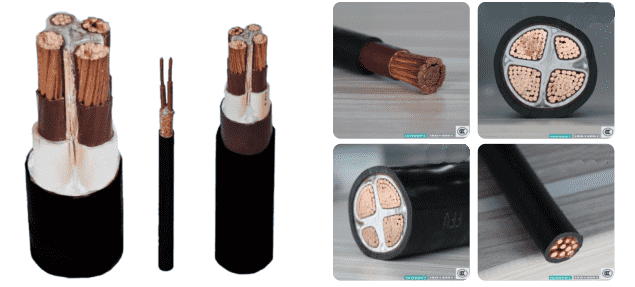
1. Single-core Cable or high-temperature wire, its structure consists of an inner conductor made of single or multi-strand copper wire (tinned copper wire), with conductor diameter of 0.42.0MM, and insulation made of fluoroplastic with insulation thickness of 0.30.5MM. Commonly used as aviation wire, for wiring in electronic and electrical equipment, and as lighting wire in special occasions.
2. Coaxial Cable Inner conductor is single or multi-strand copper (tinned copper or silver-plated copper wire), with diameter of 1.251.6MM. There are three insulation forms: A. Fluoroplastic insulation with thickness of 0.50.7MM; B. Foamed fluoroplastic insulation with thickness of 2.53.0MM; C. Combination insulation of fluoroplastic and polyethylene, i.e., inner layer using fluoroplastic insulation and outer layer using polyethylene insulation, where the fluoroplastic thickness is 0.040.07MM. This type of cable is commonly used as RF cable and connection wire for electronic equipment.
3. Multi-core Cable Single-core wires or coaxial cables twisted together form multi-core cables. Some are twisted pairs and some are non-twisted pairs, used for industrial computer control and automated instrumentation control. For special applications such as Category 5, Enhanced Category 5 cables, data transmission, audio and video transmission, etc., these fluoroplastic cables are also used.
Characteristics: Fluoroplastic has high chemical stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, fire resistance, high-temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and other characteristics. Therefore, it has wide applications in the wire and cable industry. Special cables such as high-temperature cables, flame-retardant cables, corrosion-resistant cables, etc., mostly use fluoroplastic as the outer sheath.
Applications: PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene or F4) not only has outstanding electrical insulation properties but also has a low dielectric constant and a particularly low loss factor within a wide range of operating temperatures and frequencies. Its dielectric strength, dielectric constant (2.3~2.1), volume resistivity, and surface resistivity remain good and are unaffected by temperature up to their glass transition temperature. They have low moisture absorption, making their dielectric properties minimally affected by humidity. The electrical properties of PTFE do not change over time. It is inert to almost all chemicals and solvents, maintaining its excellent properties even at high temperatures and pressures, and is particularly suitable for data transmission cables requiring low attenuation.
Therefore, in situations requiring both high-temperature resistance and fire prevention, using PTFE as RF cable insulation medium helps improve the quality of transmitted signals. PTFE polymer is used for both the insulation layer and outer sheath.
PTFE insulated wires and cables are mainly used for: heating conductors in household appliances; self-controlled cables for electrical detection in chemical equipment; connecting wires for halogen lamp bulb fixation brackets; thermocouple wires; special data recording cables for oil well drilling equipment, etc. They are also used in engineering machinery cables, and their application areas continue to expand.
Fluoroplastic cables have been increasingly used in industrial automation control. In high-temperature environments such as metallurgy, petrochemical, steel, power plants, etc., fluoroplastic cables are a good choice. In addition, due to their flame retardancy and low smoke emission during combustion, fluoroplastic cables can be widely used for general wiring in high-rise buildings, underground shopping centers, tunnels, hotels, and hospitals.
