Choosing the correct battery cable gauge is one of the most critical decisions you'll make when replacing your vehicle's wiring. Using a cable that's too thin can cause overheating, voltage drop, and poor performance. In contrast, selecting the right size ensures your vehicle starts reliably and its electrical system runs safely.
This guide provides a detailed breakdown of battery cable sizing, including essential charts and practical tips for making the right choice.
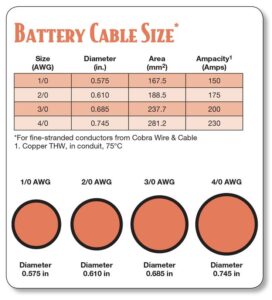
battery wire size chart
Understanding Battery Cable Gauges
In the world of electrical wiring, the gauge refers to the wire's thickness. The measurement system uses the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard, where a lower AWG number indicates a thicker wire.
For car battery cables, a thicker wire is better because it has less electrical resistance. This allows it to carry the high amperage needed to start your engine without causing a significant voltage drop.
Battery Cable Sizing Chart: By Engine and Current
To help you find the right size, use this chart as a starting point. It considers two key factors: your engine's size (in liters) and the approximate current required to start it.
For most cars and light trucks, a 2 AWG or 4 AWG cable is sufficient. Heavy-duty trucks, diesel engines, and vehicles with high-performance engines may require 0 AWG or 00 AWG to handle the massive starting current.
Adjusting for Cable Length
The distance between your battery and your starter also affects your cable choice. A longer cable has more resistance, which can lead to a significant voltage drop.
If your battery cable run is longer than the standard four to six feet, you should use a thicker gauge to compensate for the extra length and resistance.
Choosing the Right Material
Battery cables are typically made from copper. However, you'll find different types of copper conductors:
- Oxygen-Free Copper (OFC): This is the highest quality copper, offering the best conductivity and flexibility.
- Copper Clad Aluminum (CCA): This is a cheaper alternative with an aluminum core coated in copper. While it's more affordable, it has higher resistance and is not recommended for high-amperage applications like battery cables.
For reliability and performance, always choose 100% copper battery cables.
Conclusion
Selecting the right battery cable is more than just picking a size; it's about matching the wire's capacity to your vehicle's needs. By using a sizing chart and considering factors like cable length and material, you can ensure your electrical system operates efficiently and safely. A properly sized cable is a small investment that can save you from a lot of trouble on the road.
For a more comprehensive look at all things battery wiring, be sure to check out our complete guide to car battery cables.